
Ex 12.1
Ex 12.1, 2
Ex 12.1, 3
Ex 12.1, 4 Important
Ex 12.1, 5
Ex 12.1, 6 Important
Ex 12.1, 7
Ex 12.1, 8 Important
Ex 12.1, 9
Ex 12.1,10 Important
Ex 12.1, 11
Ex 12.1, 12
Ex 12.1, 13
Ex 12.1, 14 Important
Ex 12.1, 15 Important
Ex 12.1, 16
Ex 12.1, 17 Important
Ex 12.1, 18
Ex 12.1, 19 Important
Ex 12.1, 20
Ex 12.1, 21 Important
Ex 12.1, 22 Important
Ex 12.1, 23
Ex 12.1, 24
Ex 12.1, 25 Important
Ex 12.1, 26
Ex 12.1, 27
Ex 12.1, 28 Important
Ex 12.1, 29
Ex 12.1, 30 Important
Ex 12.1, 31 You are here
Ex 12.1, 32 Important
Last updated at May 7, 2024 by Teachoo


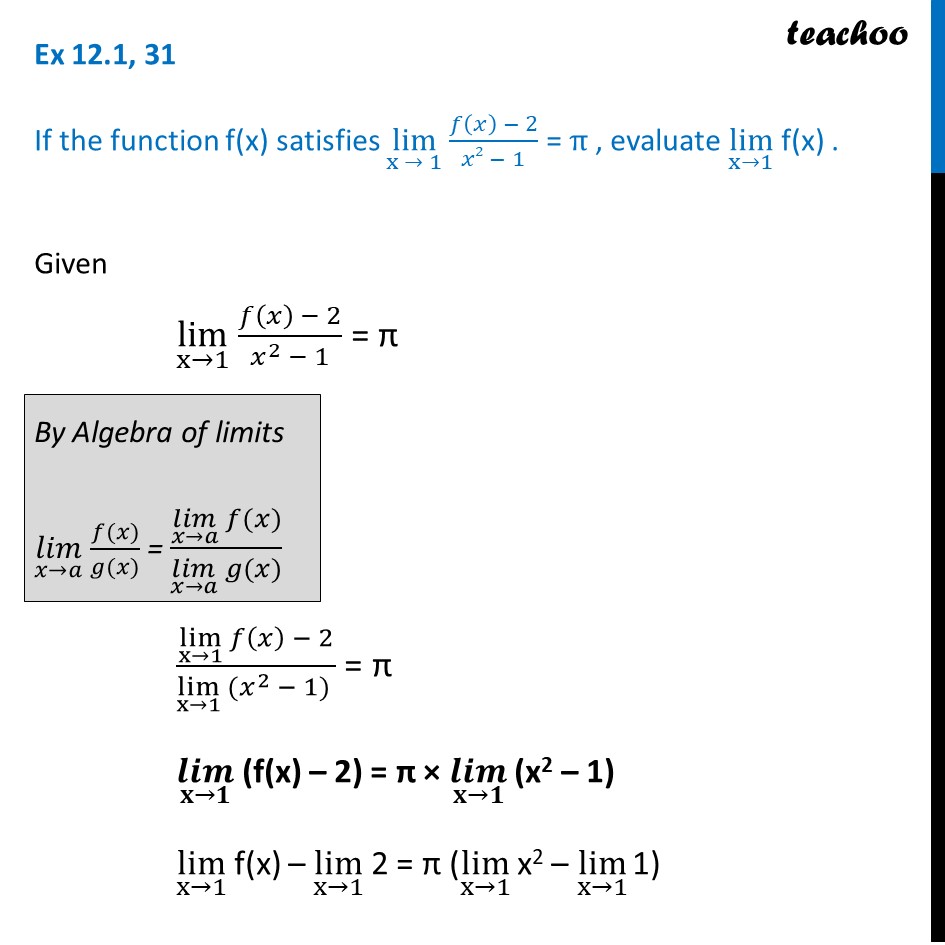
Ex 12.1, 31 If the function f(x) satisfies lim┬(x → 1) (𝑓(𝑥) − 2)/(𝑥2 − 1) = π , evaluate lim┬(x→1) f(x) . Given lim┬(x→1) (𝑓(𝑥) − 2)/(𝑥^2 − 1) = π (lim┬(x→1) 𝑓(𝑥) − 2)/(lim┬(x→1) 〖(𝑥〗^2 − 1) ) = π lim┬(x→1) (f(x) – 2) = π × lim┬(x→1) (x2 – 1) lim┬(x→1) f(x) – lim┬(x→1) 2 = π (lim┬(x→1) x2 – lim┬(x→1) 1) By Algebra of limits (𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(𝑥→𝑎) (𝑓(𝑥))/(𝑔(𝑥)) = ((𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(𝑥→𝑎) 𝑓(𝑥))/((𝑙𝑖𝑚)┬(𝑥→𝑎) 𝑔(𝑥)) (lim┬(x→1) 𝑓(𝑥) − 2)/(lim┬(x→1) 〖(𝑥〗^2 − 1) ) = π lim┬(x→1) (f(x) – 2) = π × lim┬(x→1) (x2 – 1) lim┬(x→1) f(x) – lim┬(x→1) 2 = π (lim┬(x→1) x2 – lim┬(x→1) 1) Finding limits, putting x = 1 lim┬(x→1) f(x) – 2 = π × ((1)2 – 1) lim┬(x→1) f(x) – 2 = π × 0 lim┬(x→1) f(x) – 2 = π × 0 lim┬(x→1) f(x) – 2 = 0 lim┬(x→1) f(x) = 2 Thus (𝒍𝒊𝒎)┬(𝐱→𝟏) f (x) = 2