Question 13 (OR 1 st question)
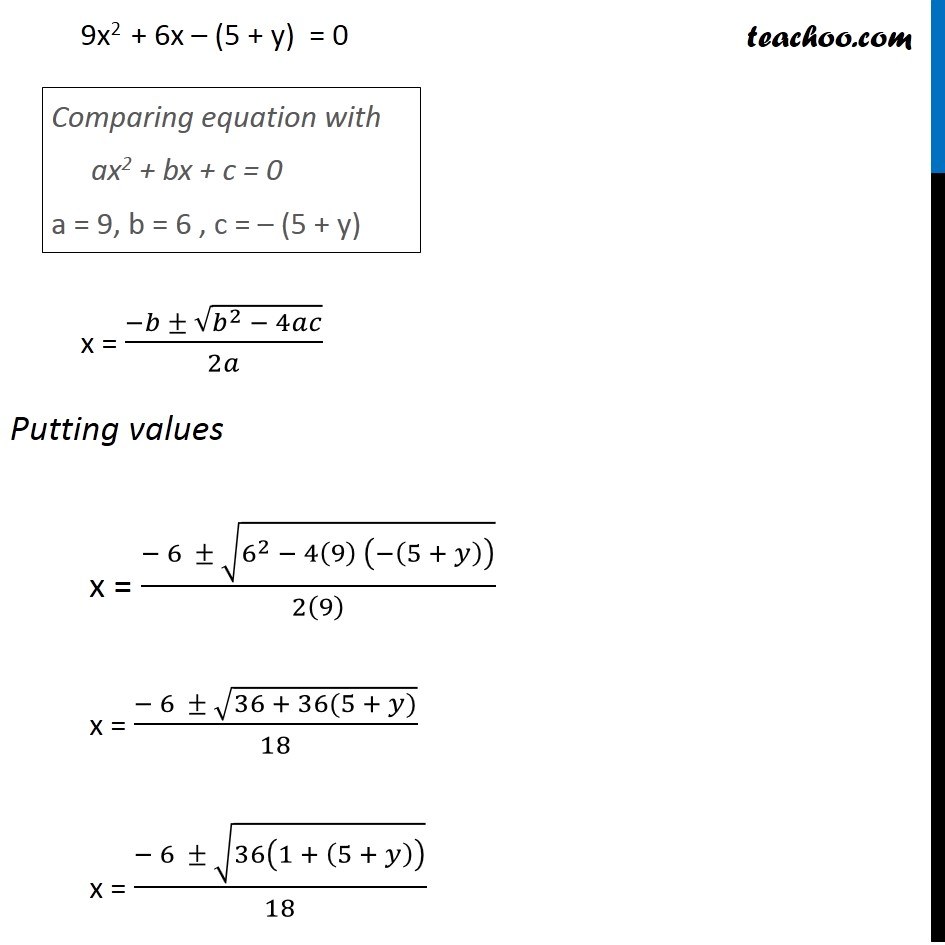
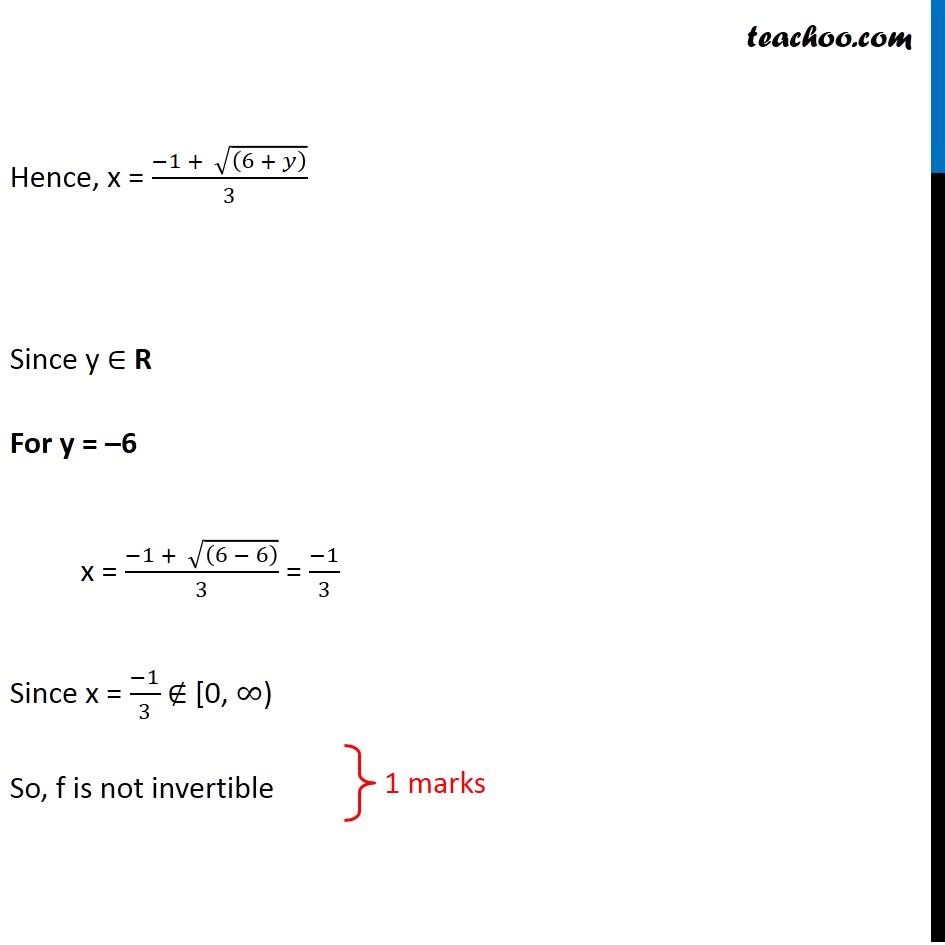
Prove that the function f:[0, ∞) → R given by f(x) = 9x 2 + 6x – 5 is not invertible. Modify the codomain of the function f to make it invertible, and hence find f –1 .







CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2019 Boards
CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2019 Boards
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo
Question 13 (OR 1 st question)
Prove that the function f:[0, ∞) → R given by f(x) = 9x 2 + 6x – 5 is not invertible. Modify the codomain of the function f to make it invertible, and hence find f –1 .









Transcript
Question 13 (OR 1st question) Prove that the function f:[0, ∞) → R given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x – 5 is not invertible. Modify the codomain of the function f to make it invertible, and hence find f–1 . If f(x) is invertible f(x) is one-one f(x) is onto First, let us check if f(x) is onto Let f(x) = y y = 9x2 + 6x – 5 0 = 9x2 + 6x – 5 – y 9x2 + 6x – 5 – y = 0 9x2 + 6x – (5 + y) = 0 Comparing equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 9, b = 6 , c = – (5 + y) x = (−𝑏 ± √(𝑏^2 − 4𝑎𝑐))/2𝑎 Putting values x = (− 6 ± √(6^2 − 4(9) (−(5 + 𝑦)) ))/2(9) x = (− 6 ± √(36 + 36(5 + 𝑦)))/18 x = (− 6 ± √(36(1 + (5 + 𝑦)) ))/18 x = (− 6 ± √(36(6 + 𝑦) ))/18 x = (− 6 ± 6 √((6 + 𝑦)))/18 x = 6[− 1 ± √((6 + 𝑦) )]/18 x = (− 1 ± √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 So, x = (− 1 − √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 or (− 1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 As x ∈ [0, ∞) , i.e., x is a positive real number x cannot be equal to (−1 − √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 Hence, x = (−1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 Since y ∈ R For y = –6 x = (−1 + √((6 − 6) ))/3 = (−1)/3 Since x = (−1)/3 ∉ [0, ∞) So, f is not invertible To make it invertible, x ≥ 0 (−1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 ≥ 0 –1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ) ≥ 0 √((6 + 𝑦) ) ≥ 0 + 1 √((6 + 𝑦) ) ≥ 1 6 + y ≥ 1 y ≥ 1 – 6 y ≥ –5 So, our range should be [–5, ∞) Now, our function is f: [0,∞) → [–5, ∞) f(x) = 9x2 + 6x – 5 We need to first check if it is one-one and onto Checking one-one f (x1) = 9(x1)2 + 6x1 – 5 f (x2) = 9(x2)2 + 6x2 – 5 Putting f (x1) = f (x2) 9(x1)2 + 6x1 – 5 = 9(x2)2 + 6x2 – 5 9(x1)2 – 9(x2)2 + 6x1 – 6x2 = – 5 + 5 9(x1)2 – 9(x2)2 + 6x1 – 6x2 = 0 Now, our function is f: [0,∞) → [–5, ∞) f(x) = 9x2 + 6x – 5 We need to first check if it is one-one and onto Checking one-one f (x1) = 9(x1)2 + 6x1 – 5 f (x2) = 9(x2)2 + 6x2 – 5 Putting f (x1) = f (x2) 9(x1)2 + 6x1 – 5 = 9(x2)2 + 6x2 – 5 9(x1)2 – 9(x2)2 + 6x1 – 6x2 = – 5 + 5 9(x1)2 – 9(x2)2 + 6x1 – 6x2 = 0 (x1 – x2) = 0 ⇒ x1 = x2 (3x1 + 3x2 + 2) = 0 ⇒ 3x1 = –3x2 – 2 Since x ∈ [0, ∞) i.e. x is always positive, Hence 3x1 = – 3x2 – 2 is not true Hence, if f (x1) = f (x2) , then x1 = x2 ∴ f is one-one Now, Checking onto f(x) = 9x2 + 6x – 5 Putting f(x) = y, We get x = (−1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 Since for y ∈ [–5, ∞) x ∈ [0, ∞) Thus, f is onto Since the function is one-one and onto ∴ It is invertible Calculating inverse For finding inverse, we put f(x) = y and find x in terms of y We have done that while proving onto x = (−1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 Let g(y) = (−1 + √((6 + 𝑦) ))/3 where g: [–5,∞ ) → [0, ∞) So, inverse of f = f–1 = (−𝟏 + √((𝟔 + 𝒚) ))/𝟑