Question 16 (OR 2 nd question)
Find the value of k for which the points (3k – 1, k – 2), (k, k – 7) and (k – 1, –k – 2) are collinear.


CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper for 2019 Boards
CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper for 2019 Boards
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo
Question 16 (OR 2 nd question)
Find the value of k for which the points (3k – 1, k – 2), (k, k – 7) and (k – 1, –k – 2) are collinear.



Transcript
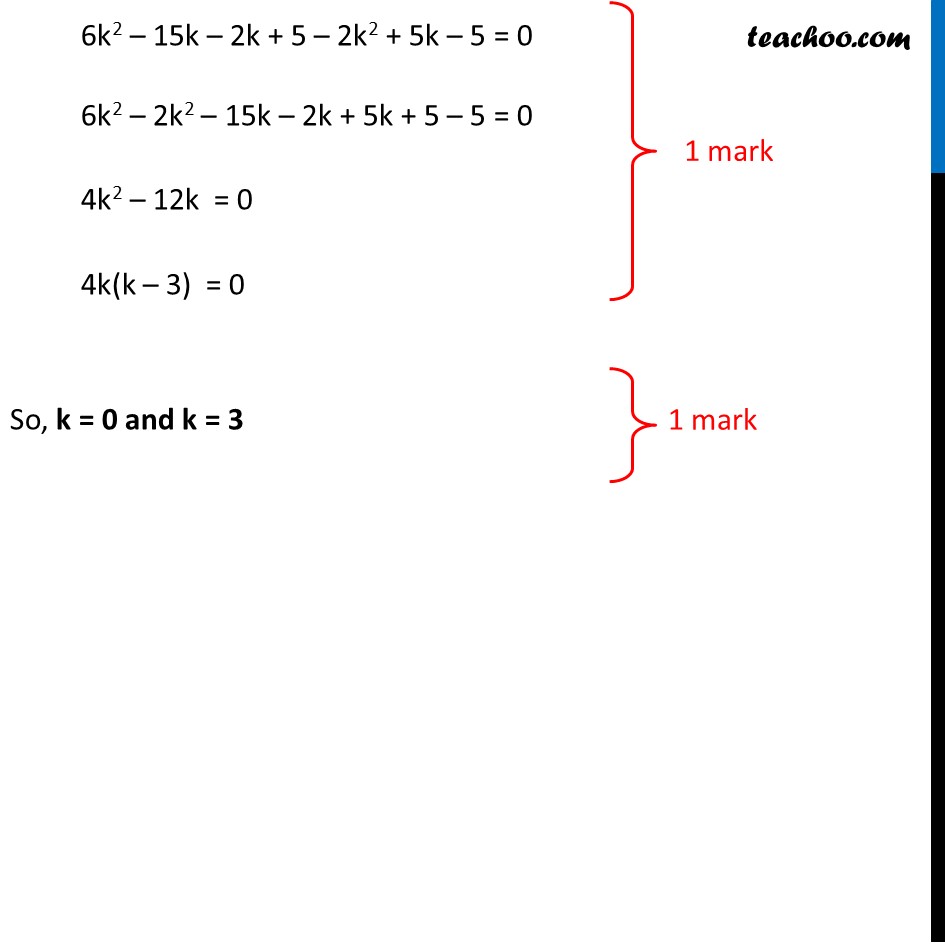
Question 16 (OR 2nd question) Find the value of k for which the points (3k – 1, k – 2), (k, k – 7) and (k – 1, –k – 2) are collinear. Let points be A (3k – 1, k – 2), B (k, k – 7) and C (k – 1, –k – 2) If A, B, C are collinear, they will lie on the same line, i.e. they will not form triangle Therefore, Area of ∆ABC = 0 1/2 [ x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2) ] = 0 1 mark Here x1 = 3k – 1 , y1 = k – 2 x2 = k , y2 = k – 7 x3 = k – 1 , y3 = −k – 2 Putting values 1/2 [ x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2) ] = 0 x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2) = 0 (3k – 1)[k – 7 – (–k – 2)] + k[−k − 2 – (k – 2)] + (k – 1)[(k – 2) – (k – 7)] = 0 (3k – 1)[k – 7 + k + 2] + k[−k − 2 – k + 2] + (k – 1)[k – 2 – k + 7] = 0 (3k – 1)(2k – 5) + k[−2k] + (k – 1)[–2 + 7] = 0 3k(2k – 5) – 1(2k – 5) – 2k2 + (k – 1)5 = 0 6k2 – 15k – 2k + 5 – 2k2 + 5k – 5 = 0 6k2 – 2k2 – 15k – 2k + 5k + 5 – 5 = 0 4k2 – 12k = 0 4k(k – 3) = 0 1 mark So, k = 0 and k = 3 1 mark