

Chapter 7 Class 12 Integrals
Chapter 7 Class 12 Integrals
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
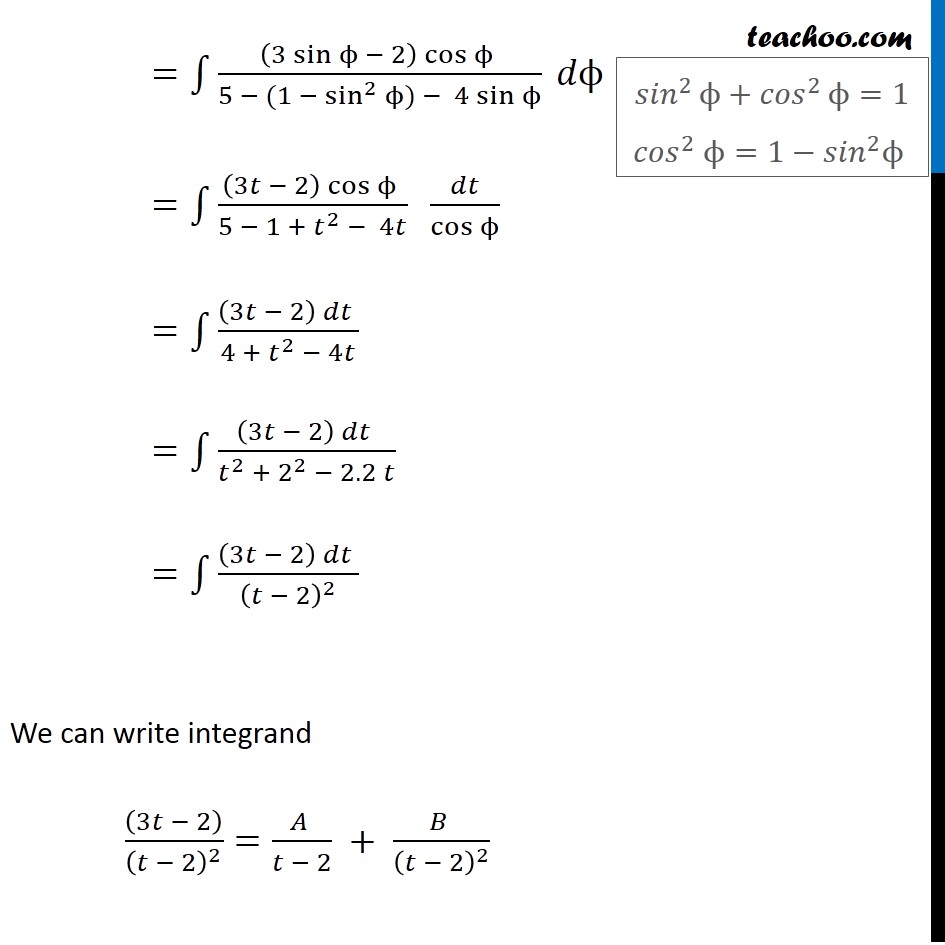
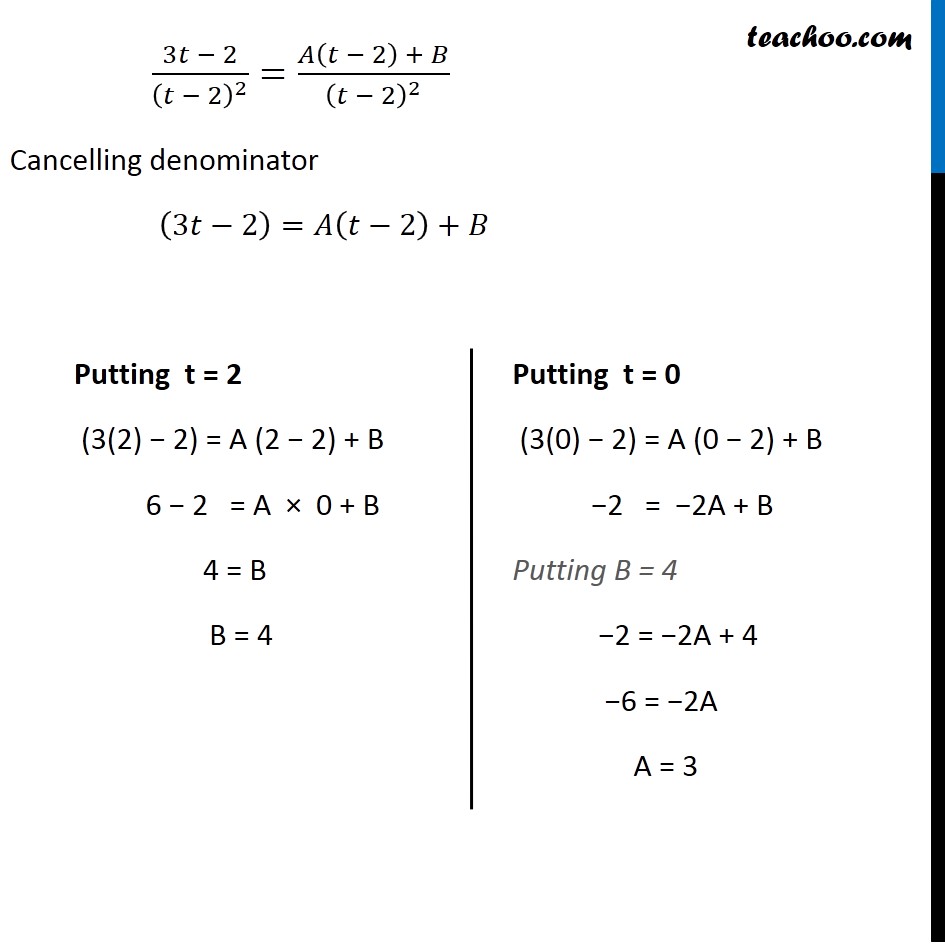
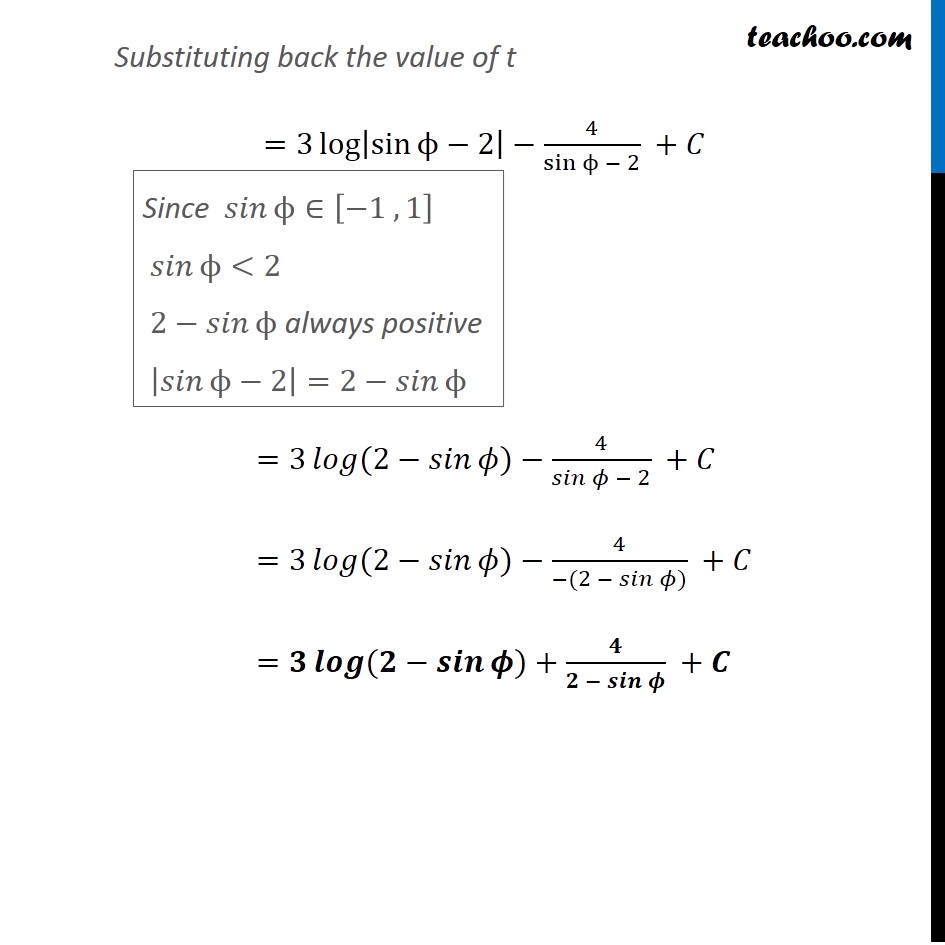
Example 15 Find ∫1▒((3 sinϕ −2) cosϕ )/(5 − cos^2ϕ − 4 sinϕ ) 𝑑ϕ Let 𝑡=sinϕ Differentiating w.r.t. ϕ 𝑑𝑡/𝑑ϕ=cosϕ 𝑑𝑡/cosϕ =𝑑ϕ Now we can write ∫1▒((3 sinϕ −2) cosϕ )/(5 − cos^2ϕ − 4 sinϕ ) 𝑑ϕ =∫1▒((3 sinϕ − 2) cosϕ )/(5 − (1 − sin^2ϕ) − 4 sinϕ ) 𝑑ϕ =∫1▒((3𝑡 − 2) cosϕ )/(5 − 1 + 𝑡^2 − 4𝑡) 𝑑𝑡/cosϕ =∫1▒((3𝑡 − 2) 𝑑𝑡 )/(4 + 𝑡^2 − 4𝑡) =∫1▒((3𝑡 − 2) 𝑑𝑡 )/(𝑡^2 + 2^2 − 2.2 𝑡) =∫1▒((3𝑡 − 2) 𝑑𝑡 )/(𝑡 − 2)^2 We can write integrand ((3𝑡 − 2))/(𝑡 − 2)^2 =(𝐴 )/(𝑡 − 2) + (𝐵 )/(𝑡 − 2)^2 〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^2ϕ+〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2ϕ=1 〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 ϕ=1−〖𝑠𝑖𝑛〗^2 ϕ (3𝑡 − 2)/(𝑡 − 2)^2 =(𝐴(𝑡 − 2) + 𝐵)/(𝑡 − 2)^2 Cancelling denominator (3𝑡−2)=𝐴(𝑡−2)+𝐵 Putting t = 2 (3(2) − 2) = A (2 − 2) + B 6 − 2 = A × 0 + B 4 = B B = 4 Putting t = 0 (3(0) − 2) = A (0 − 2) + B −2 = −2A + B Putting B = 4 −2 = −2A + 4 −6 = −2A A = 3 Hence, we can write it as ((3𝑡 − 2))/(𝑡 − 2)^2 =(𝐴 )/(𝑡 − 2) + (𝐵 )/(𝑡 − 2)^2 ((3𝑡 − 2))/(𝑡 − 2)^2 = 3/(𝑡 − 2) + 4/(𝑡 − 2)^2 Now, our equation becomes ∫1▒(3𝑡 − 2)/(𝑡 − 2)^2 𝑑𝑡=∫1▒3/(𝑡 − 2) 𝑑𝑡+∫1▒4/(𝑡 − 2)^2 𝑑𝑡 =3 log|𝑡−2|+4×(𝑡 − 2)^(−1)/(−1) +𝐶 =3 log|𝑡−2|−4×1/((𝑡 − 2) ) +𝐶 Substituting back the value of t =3 log|sinϕ−2|−4/(sinϕ − 2) +𝐶 =3 𝑙𝑜𝑔〖(2−𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜙)〗−4/(𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜙 − 2) +𝐶 =3 𝑙𝑜𝑔〖(2−𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜙)〗−4/(−(2 − 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜙)) +𝐶 =𝟑 𝒍𝒐𝒈〖(𝟐−𝒔𝒊𝒏𝝓)〗+𝟒/(𝟐 − 𝒔𝒊𝒏𝝓 ) +𝑪 Since 𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ∈[−1 , 1] 𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ<2 2−𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ always positive |𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ−2|=2−𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ