

Integration by substitution - Trignometric - Normal
Integration by substitution - Trignometric - Normal
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
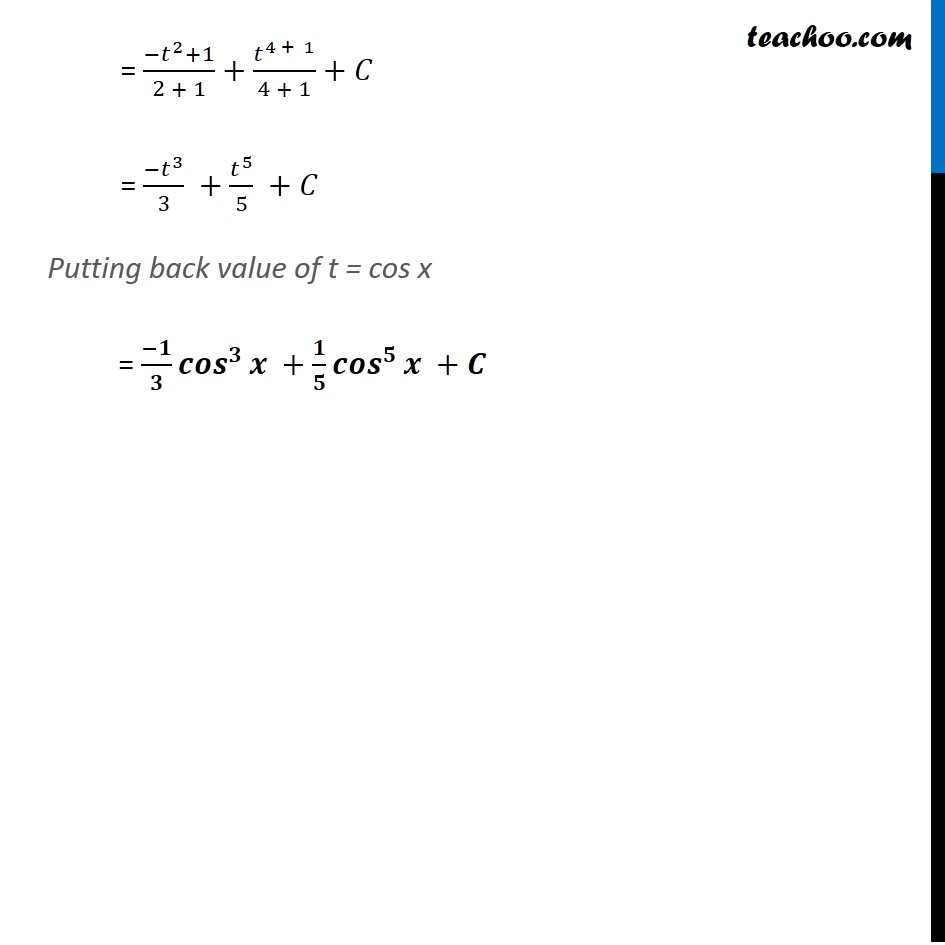
Example 6 Find the following integrals: (i) ∫1▒〖sin^3𝑥 cos^2𝑥 〗 𝑑𝑥 ∫1▒〖sin^3𝑥 cos^2𝑥 〗 𝑑𝑥 Let cos 𝑥=𝑡 Differentiating both sides 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥. −sin𝑥=𝑑𝑡/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥=(−𝑑𝑡)/sin𝑥 Now are equation becomes ∫1▒〖sin^3𝑥 cos^2𝑥 〗 𝑑𝑥 Putting value of 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 and 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1▒sin^3𝑥 .𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑥 = ∫1▒sin^3𝑥 .𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑡/(−sin𝑥 ) = ∫1▒sin^3𝑥/(−sin𝑥 ) 𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑡 = –∫1▒sin^2𝑥 𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑡 = – ∫1▒(1−cos^2𝑥 ) 𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑡 = – ∫1▒(1−𝑡^2 ) 𝑡^2. 𝑑𝑡 = – ∫1▒(𝑡^2−𝑡^4 ) 𝑑𝑡 = ∫1▒(−𝑡^2+𝑡^4 ) 𝑑𝑡 = ∫1▒〖−𝑡^2 〗. 𝑑𝑡 + ∫1▒𝑡^4 . 𝑑𝑡 (∴ sin^2𝑥=1−cos^2𝑥) = (〖−𝑡〗^2+1)/(2 + 1)+𝑡^(4 + 1)/(4 + 1)+𝐶 = (−𝑡^3)/3 +𝑡^5/5 +𝐶 Putting back value of t = cos x = (−𝟏)/𝟑 〖𝒄𝒐𝒔〗^𝟑𝒙 +𝟏/𝟓 〖𝒄𝒐𝒔〗^𝟓𝒙 +𝑪