


Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo





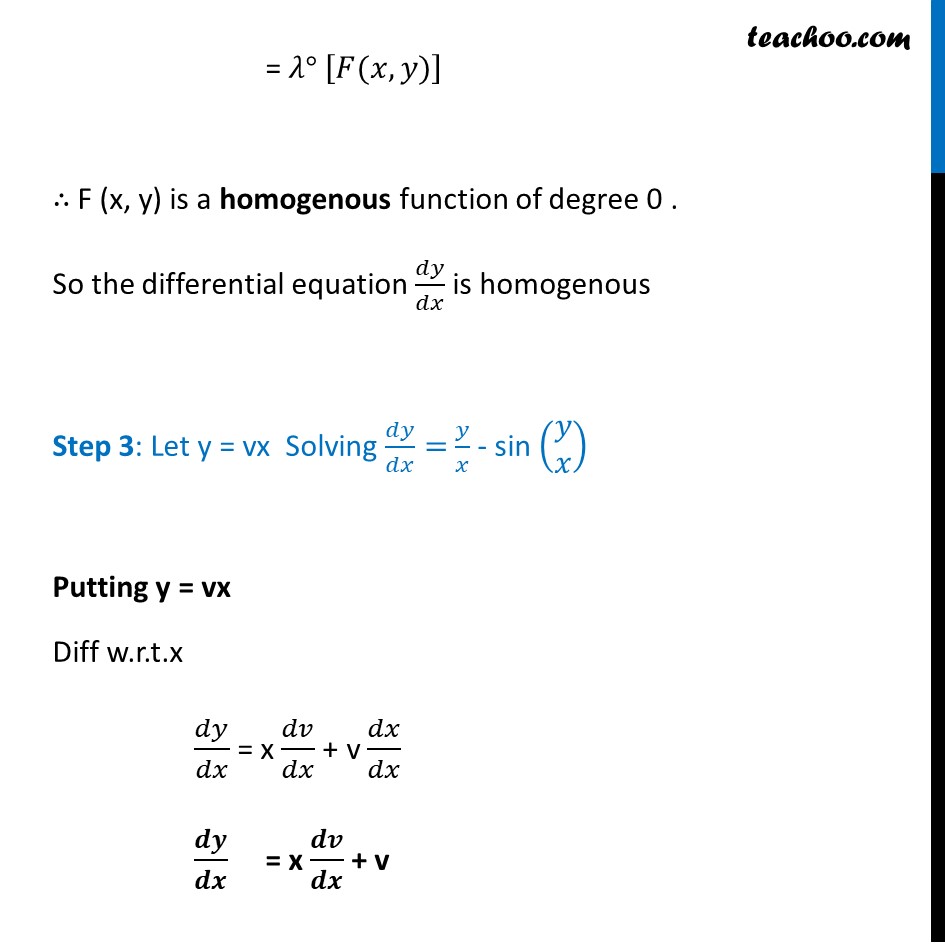
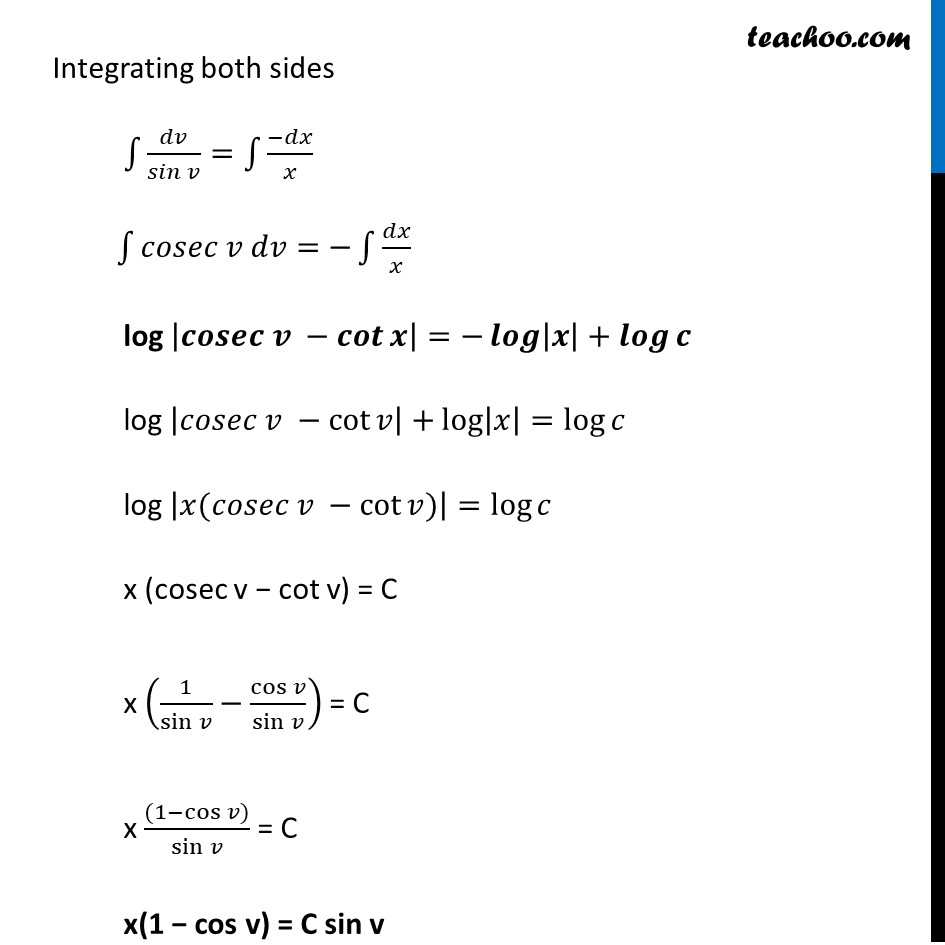
Ex 9.4, 8 show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve each of them. 𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥−𝑦+𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑦/𝑥)=0 Step 1: Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 𝒙 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙 = y − x sin (𝒚/𝒙) Step 2: Put 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = F (x, y) and find F(𝜆x, 𝜆y) F(x, y) = 𝑦/𝑥 − sin (𝑦/𝑥) F(𝜆x, 𝜆y) = ("𝜆" 𝑦)/("𝜆" 𝑥) − sin (("𝜆" 𝑦)/("𝜆" 𝑥)) = 𝑦/𝑥 − sin (𝑦/𝑥) = F(x, y) = 𝜆° [𝐹(𝑥, 𝑦)] ∴ F (x, y) is a homogenous function of degree 0 . So the differential equation 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 is homogenous Step 3: Let y = vx Solving 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥= 𝑦/𝑥 - sin (█(𝑦@𝑥)) Putting y = vx Diff w.r.t.x 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = x 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 + v 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑥 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒙 = x 𝒅𝒗/𝒅𝒙 + v Putting value of 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑥2 + 𝑦^2)/(𝑥2 + 𝑥𝑦) and y = vx in (1) 𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = y − x sin (𝑦/𝑥) v + (𝒙 𝒅𝒗)/𝒅𝒙 = 𝒗𝒙/𝒙 − sin (𝒗𝒙/𝒙) v + (𝑥 𝑑𝑣)/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑣 − sin v (𝑥 𝑑𝑣)/𝑑𝑥 = v − sin v − v (𝑥 𝑑𝑣)/𝑑𝑥 = −sin𝑣 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 = (−sin𝑣)/𝑥 𝒅𝒗/(𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒗) = (−𝒅𝒙)/𝒙 Integrating both sides ∫1▒〖𝑑𝑣/(𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝑣)=∫1▒(−𝑑𝑥)/𝑥〗 ∫1▒〖𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑣 𝑑𝑣=−∫1▒𝑑𝑥/𝑥 〗 log |𝒄𝒐𝒔𝒆𝒄 𝒗 −𝒄𝒐𝒕𝒙 |=−𝒍𝒐𝒈|𝒙|+𝒍𝒐𝒈𝒄 log |𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑣 −cot𝑣 |+log|𝑥|=log𝑐 log |𝑥(𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑣 −cot〖𝑣)〗 |=log𝑐 x (cosec v − cot v) = C x (1/sin𝑣 −cos𝑣/sin𝑣 ) = C x ((1−cos〖𝑣)〗)/sin𝑣 = C x(1 − cos v) = C sin v Putting value of v = 𝑦/𝑥 x(𝟏−𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝒚/𝒙)) = C sin (𝒚/𝒙)