


Examples
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
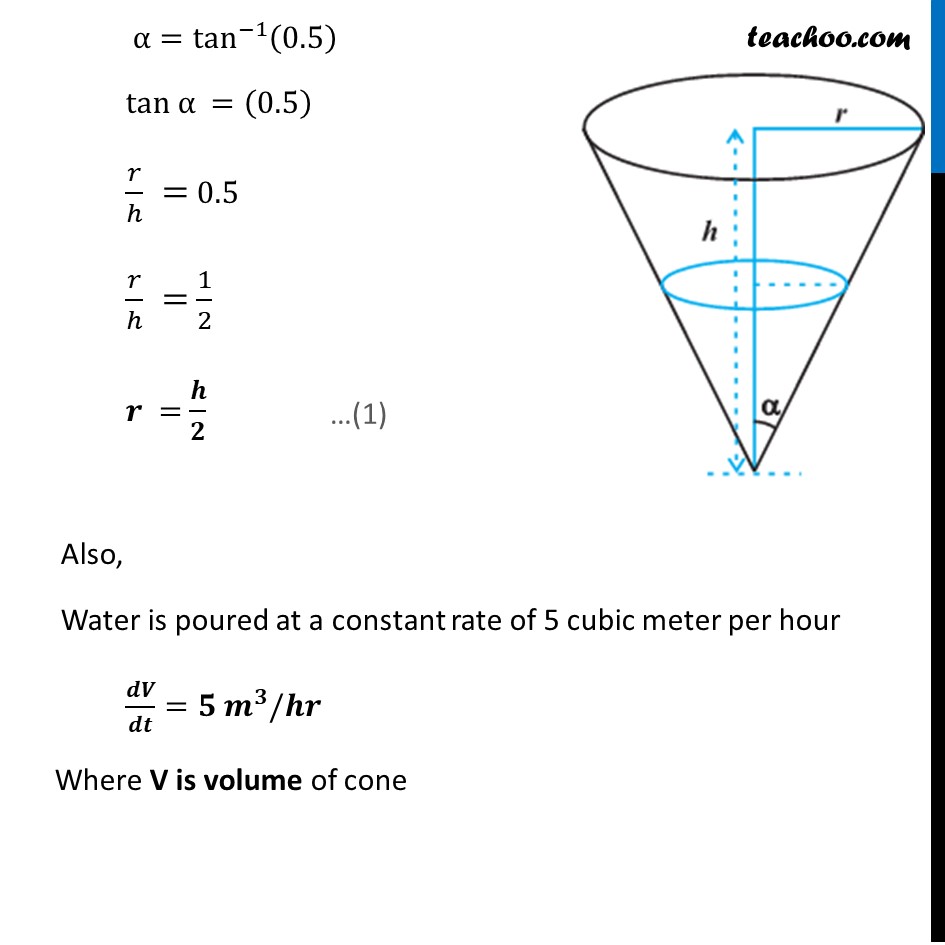
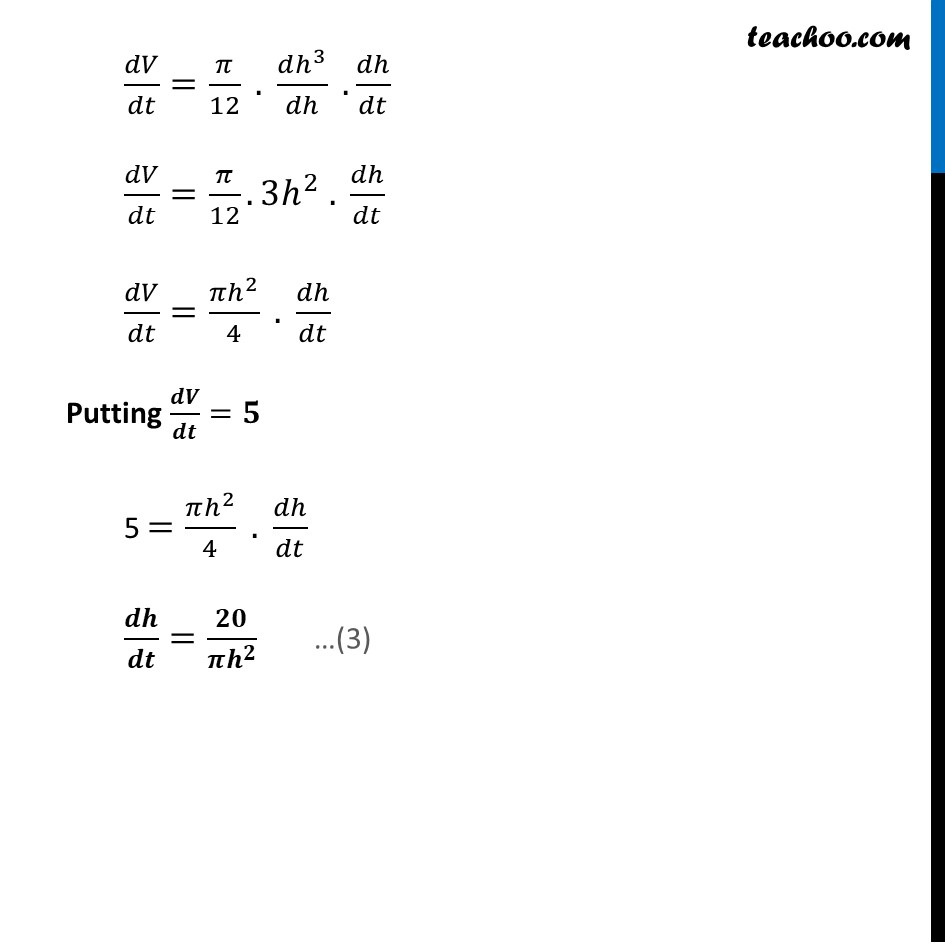
Example 31 A water tank has the shape of an inverted right circular cone with its axis vertical and vertex lowermost. Its semi-vertical angle is tan–1 (0.5). Water is poured into it at a constant rate of 5 cubic meter per hour. Find the rate at which the level of the water is rising at the instant when the depth of water in the tank is 4 m.Water tank is in shape of cone Let r be the radius of cone, h be the height of cone, & 𝜶 be the semi−vertical angle Given Semi-vertical angle is tan^(−1)(0.5) α=tan^(−1)(0.5) tan α =(0.5) 𝑟/ℎ = 0.5 𝑟/ℎ = 1/2 𝒓 = 𝒉/𝟐 Also, Water is poured at a constant rate of 5 cubic meter per hour 𝒅𝑽/𝒅𝒕=𝟓 𝒎^𝟑/𝒉𝒓 Where V is volume of cone Now, 𝑉=1/3 𝜋𝑟^2 ℎ 𝑉=1/3 𝜋(𝒉/𝟐)^2 ℎ 𝑉=1/3 𝜋(〖h/4〗^2 )ℎ 𝑽=(𝝅𝒉^𝟑)/𝟏𝟐 Differentiate w.r.t. t 𝑑𝑉/𝑑𝑡=𝑑((𝜋ℎ^3)/12)/𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑉/𝑑𝑡=𝜋/12 . (𝑑ℎ^3)/𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑉/𝑑𝑡=𝜋/12 . (𝑑ℎ^3)/𝑑ℎ .𝑑ℎ/𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑉/𝑑𝑡=𝜋/12. 3ℎ^2 . 𝑑ℎ/𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑉/𝑑𝑡=(𝜋ℎ^2)/4 . 𝑑ℎ/𝑑𝑡 Putting 𝒅𝑽/𝒅𝒕=𝟓 5 =(𝜋ℎ^2)/4 . 𝑑ℎ/𝑑𝑡 𝒅𝒉/𝒅𝒕=𝟐𝟎/(𝝅𝒉^𝟐 ) We need to find, Rate at which level of water is rising when depth is 4 m i.e. ├ 𝒅𝒉/𝒅𝒕┤|_(𝒉 = 𝟒 𝒎) Putting h = 4 m in (3) ├ 𝑑ℎ/𝑑𝑡┤|_(ℎ = 4𝑚)=20/(𝜋(ℎ)^2 )=20/16 × 1/𝜋=5/4 × 1/(22/7)=5/4 × 7/22=35/88 Hence, rate of change of water level is 𝟑𝟓/𝟖𝟖 m/hr.