

Conditional Probability - Values given
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo



Transcript
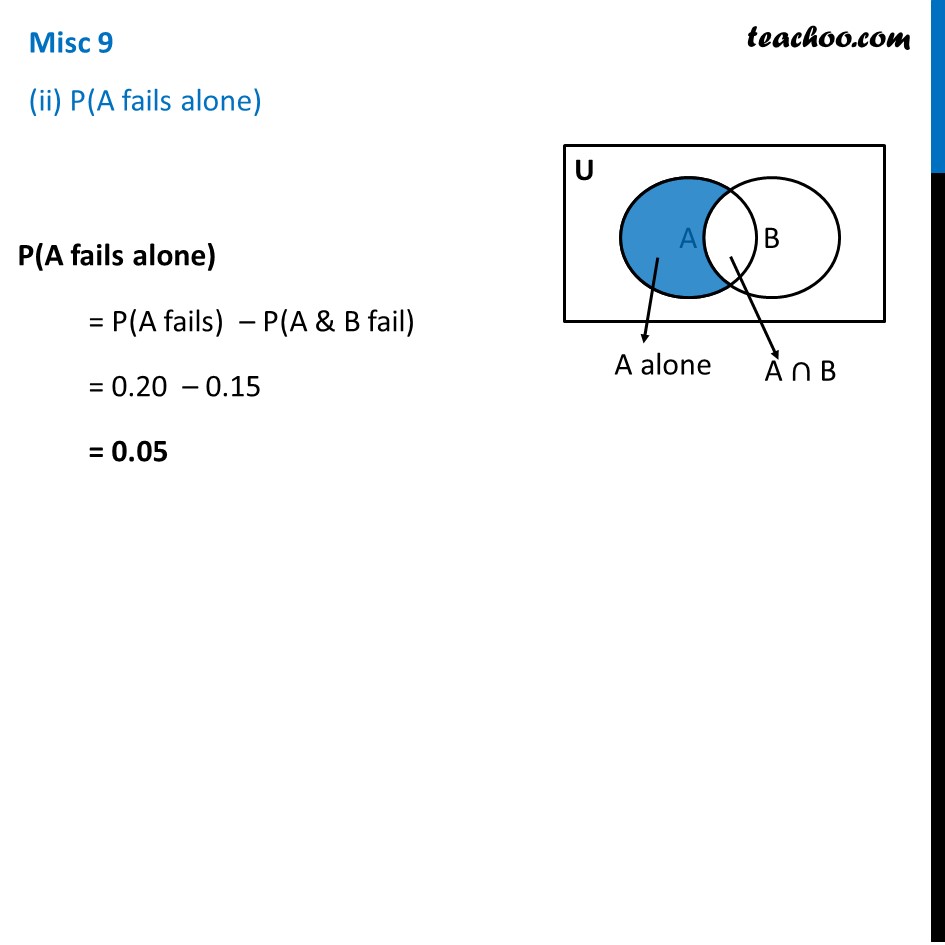
Misc 9 An electronic assembly consists of two subsystems, say, A and B. From previous testing procedures, the following probabilities are assumed to be known: P(A fails) = 0.2 P(B fails alone) = 0.15 P(A and B fail) = 0.15 Evaluate the following probabilities (i) P(A fails |B has failed) Finding P(B fails) P(B fails alone) = P(B fails) – P(A & B fail) 0.15 = P(B fails) – 0.15 0.15 + 0.15 = P(B fails) 0.30 = P(B fails) P(B fails) = 0.30 Now, P(A fails |B has failed) = (𝑷(𝑨 & 𝑩 𝑭𝒂𝒊𝒍))/(𝑷(𝑩 𝑭𝒂𝒊𝒍)) = (0. 15)/(0. 30) = 1/2 = 0.5 ∴ P(A fails |B has failed) = 0.5 Misc 9 (ii) P(A fails alone) P(A fails alone) = P(A fails) – P(A & B fail) = 0.20 – 0.15 = 0.05