

Binomial Distribution
Binomial Distribution
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
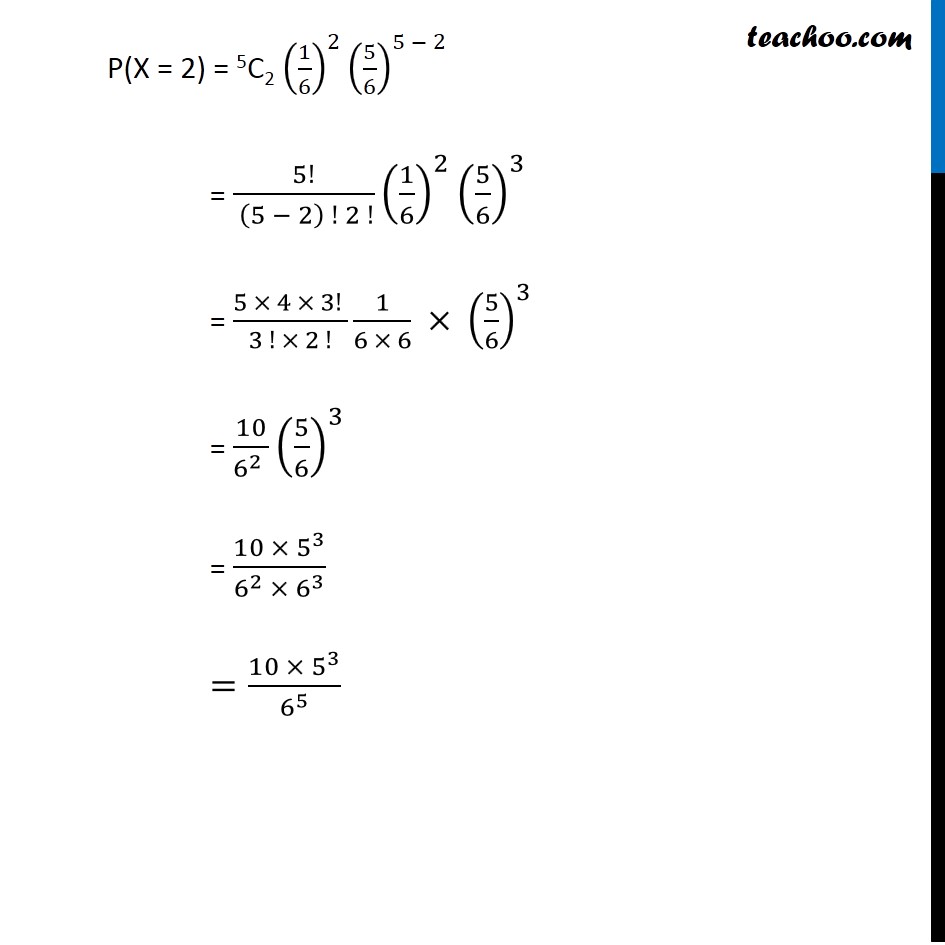
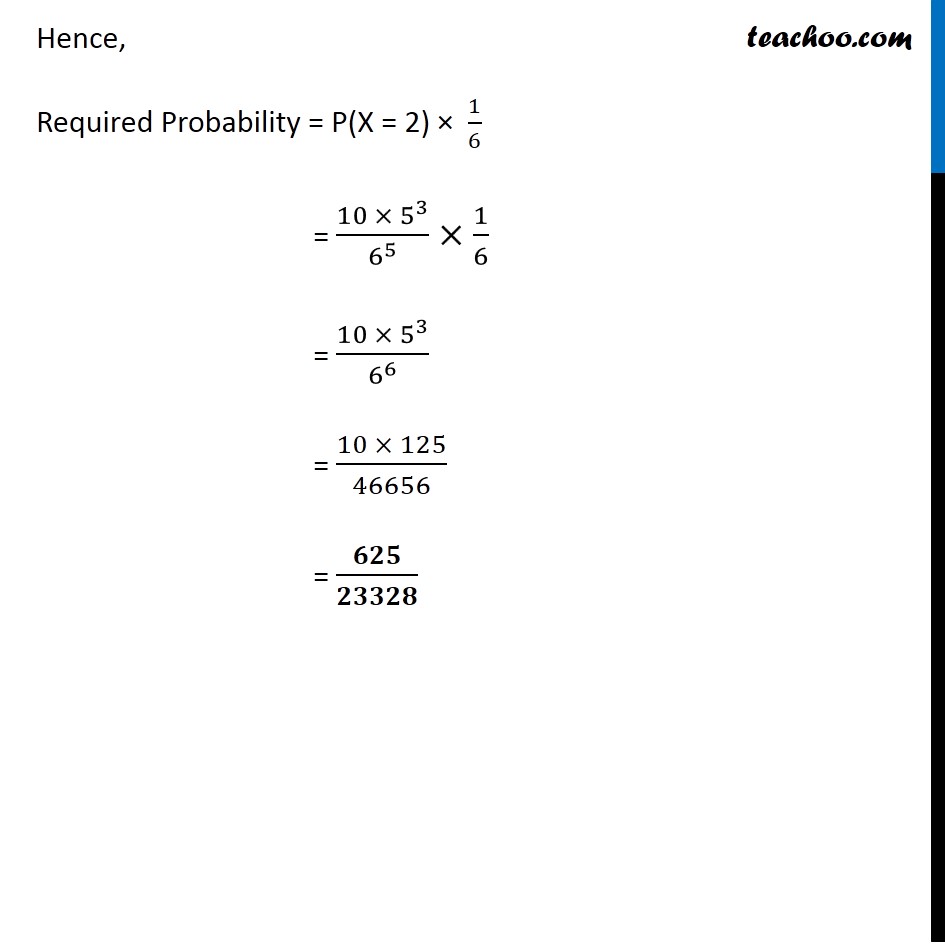
Question 3 A die is thrown again and again until three sixes are obtained. Find the probability of obtaining the third six in the sixth throw of the die. We need to find probability of obtaining the third six in the sixth throw of the die. P(getting 3rd six in 6th throw) = P(getting 2 sixes in 5 throws) × P(getting a six on 6th throw) = P(getting 2 sixes in 5 throws) × 1/6 Calculating P(getting 2 sixes in 5 throws) Let X : be the number six we get on 5 throws Throwing a pair of die is a Bernoulli trial So, X has binomial distribution P(X = x) = nCx 𝒒^(𝒏−𝒙) 𝒑^𝒙 Here n = number of times die is thrown = 5 p = Probability of getting a six = 1/6 q = 1 – 1/6 = 5/6 Hence, P(X = x) = 5Cx (𝟏/𝟔)^𝒙 (𝟓/𝟔)^(𝟓 − 𝒙) We need to find P(getting 2 sixes in 5 throws) i.e. P(X = 2) P(X = 2) = 5C2 (1/6)^2 (5/6)^(5 − 2 ) = 5!/( (5 − 2) ! 2 !) (1/6)^2 (5/6)^3 = (5 × 4 × 3! )/(3 ! × 2 !) 1/(6 × 6) × (5/6)^3 = 10/(6^2 ) (5/6)^3 = (10 ×〖 5〗^3)/(6^2 × 6^3 ) =(10 ×〖 5〗^3)/6^5 Hence, Required Probability = P(X = 2) × 1/6 = (10 ×〖 5〗^3)/6^5 ×1/6 = (10 ×〖 5〗^3)/6^6 = (10 × 125)/46656 = 𝟔𝟐𝟓/𝟐𝟑𝟑𝟐𝟖