




Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo








Transcript
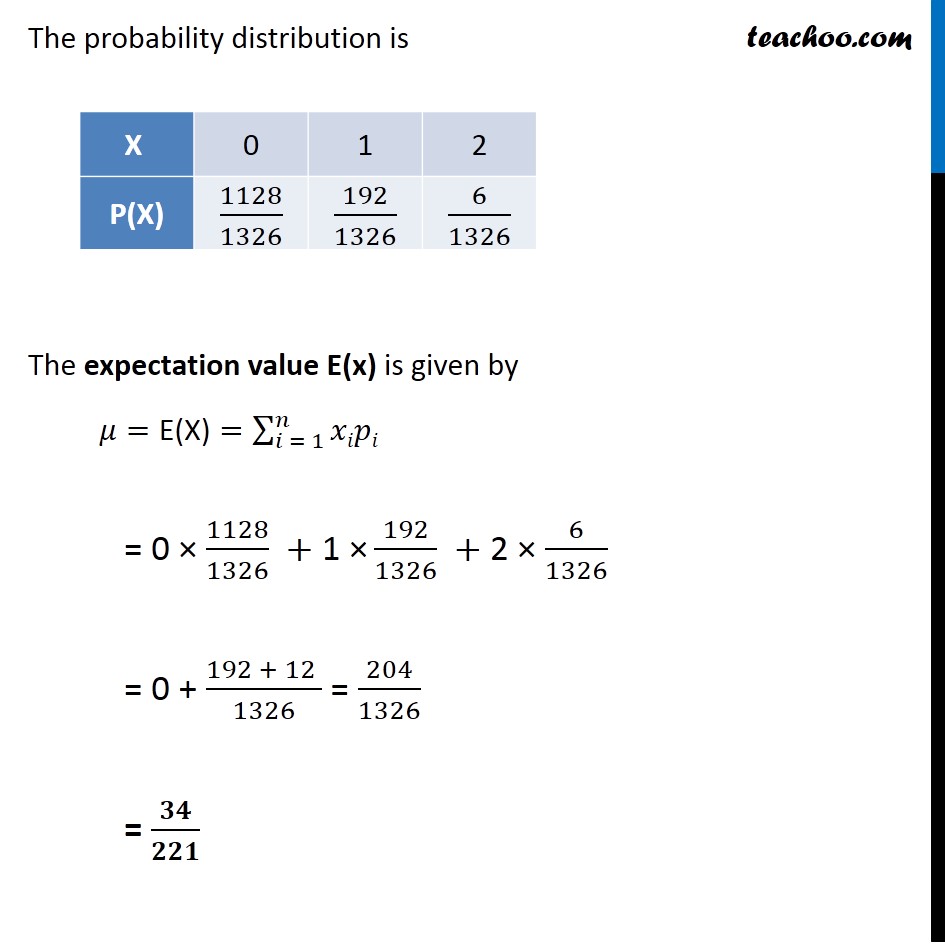
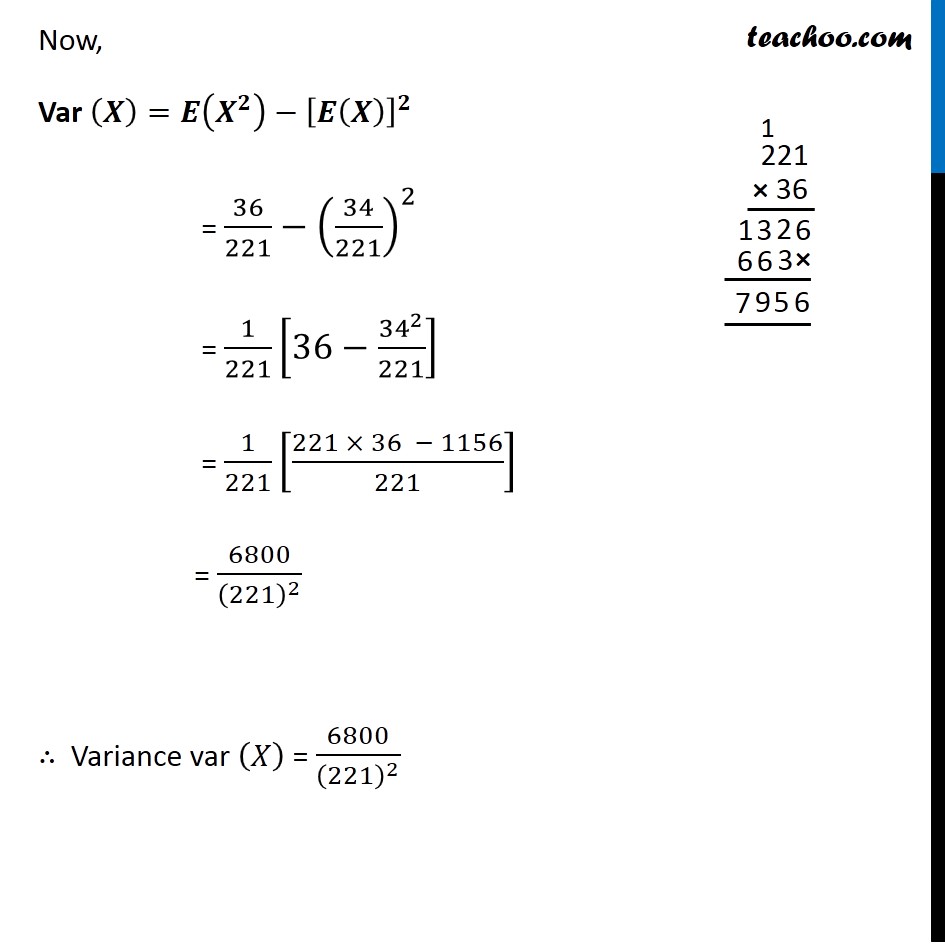
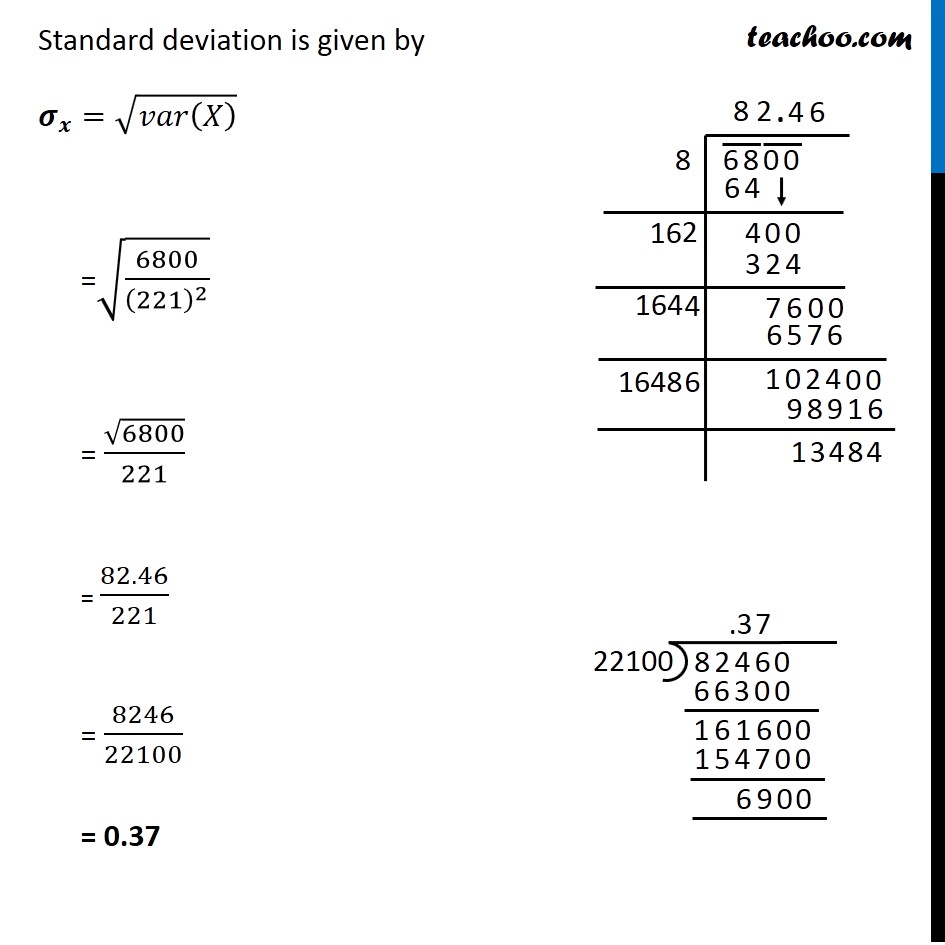
Question 8 Two cards are drawn simultaneously (or successively without replacement) from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the mean, variance and standard deviation of the number of kings.Since we are drawing cards without replacement, it is NOT a Bernoulli trial Let X be the number of kings obtained We can get 0, 1, or 2 kings So, value of X is 0, 1 or 2 Total number of ways to draw 2 cards out of 52 is Total ways = 52C2 = 1326 P(X = 0) i.e. Probability of getting 0 kings Number of ways to get 0 kings = Number of ways to select 2 cards out of non king cards = Number of ways to select 2 cards out of (52 – 4) 48 cards = 48C2 = 1128 P(X = 0) = (𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑔𝑒𝑡 0 𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠)/(𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠) = 1128/1326 P(X = 1) i.e. Probability of getting 1 kings Number of ways to get 1 kings = Number of ways to select 1 king out of 4 king cards × Number of ways to select 1 card from 48 non king cards = 4C1 × 48C1 = 4 × 48 = 192 P(X = 1) = (𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑔𝑒𝑡 1 𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔)/(𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠) = 192/1326 P(X = 2) i.e. Probability of getting 2 kings Number of ways to get 1 kings = Number of ways of selecting 2 kings out of 4 king cards = 4C2 = 6 P(X = 2) = (𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑔𝑒𝑡 2 𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠)/(𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠) = 6/1326 The probability distribution is The expectation value E(x) is given by 𝜇="E(X)"=∑2_(𝑖 = 1)^𝑛▒𝑥𝑖𝑝𝑖 = 0 × 1128/1326 +"1 ×" 192/1326 + 2 × 6/1326 = 0 + (192 + 12 )/1326 = 204/1326 = 𝟑𝟒/𝟐𝟐𝟏 The variance of x is given by : Var (𝑋)=𝐸(𝑋^2 )−[𝐸(𝑋)]^2 So, finding 𝑬(𝑿^𝟐 ) E(𝑋^2 )=∑2_(𝑖 = 1)^𝑛▒〖〖𝑥_𝑖〗^2 𝑝𝑖〗 = 02 × 1128/1326+"12 × " 192/1326+ 22 × 6/1326 = 0+(192 + 4 × 6)/1326 = (192 + 24)/1326 = 216/1326 = 36/221 Now, Var (𝑿)=𝑬(𝑿^𝟐 )−[𝑬(𝑿)]^𝟐 = 36/221−(34/221)^2 = 1/221 [36−〖34〗^2/221] = 1/221 [(221 × 36 − 1156)/221] = 6800/(221)^2 ∴ Variance var (𝑋) = 6800/(221)^2 Standard deviation is given by 𝝈_𝒙=√(𝑣𝑎𝑟(𝑋) ) =√(6800/(221)^2 ) = √6800/221 = 82.46/221 = 8246/22100 = 0.37