


Examples
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
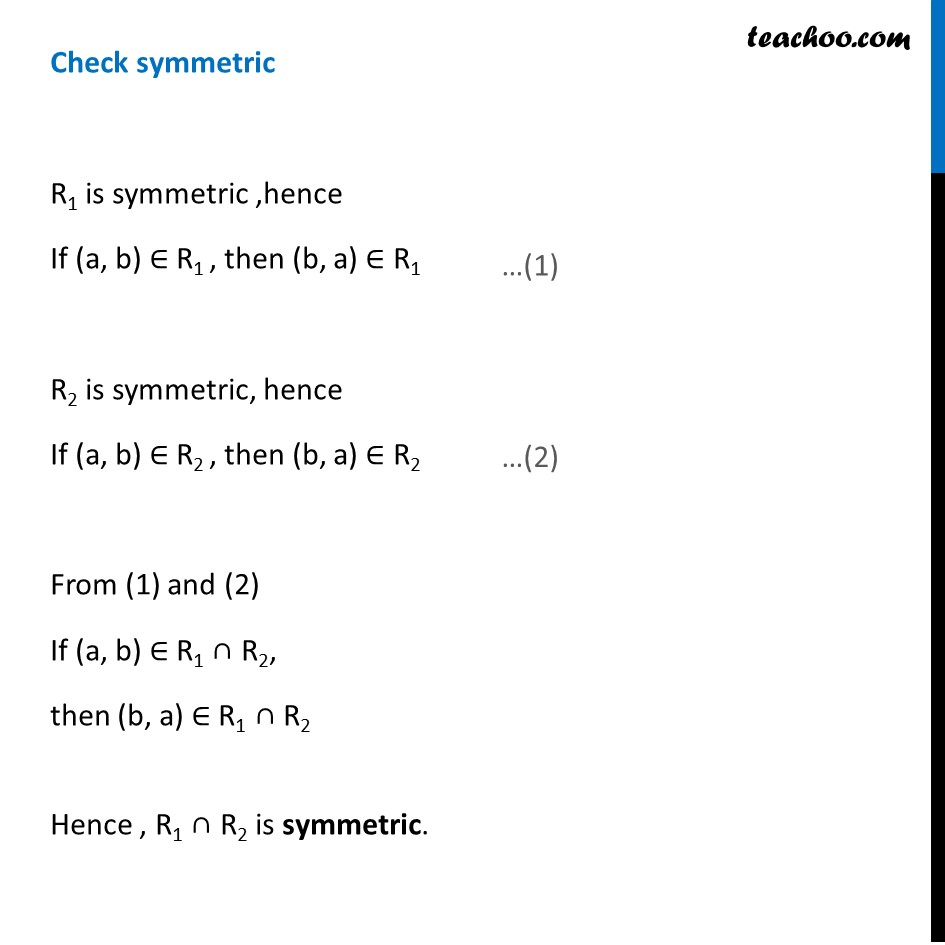
Example 18 If R1 and R2 are equivalence relations in a set A, show that R1 ∩ R2 is also an equivalence relation. R1 is an equivalence relation 1. R1 is symmetric (a, a) ∈ R1, for all a ∈ A. 2. R1 is reflexive If (a, b) ∈ R1 , then (b, a) ∈ R1 3. R1 is transitive If (a, b) ∈ R1 & (b, c) ∈ R1 , then (a, c) ∈ R1 R2 is an equivalence relation 1. R2 is symmetric (a, a) ∈ R2, for all a ∈ A. 2. R2 is reflexive If (a, b) ∈ R2 , then (b, a) ∈ R2 3. R2 is transitive If (a, b) ∈ R2 & (b, c) ∈ R2 , then (a, c) ∈ R2 We have to prove R1 ∩ R2 is equivalence relation Check reflexive For all a ∈ A (a, a) ∈ R1, & (a, a) ∈ R2 Hence, (a, a) ∈ both R1 & R2 Hence, (a, a) ∈ R1 ∩ R2 ∴ R1 ∩ R2 is reflexive. Check symmetric R1 is symmetric ,hence If (a, b) ∈ R1 , then (b, a) ∈ R1 R2 is symmetric, hence If (a, b) ∈ R2 , then (b, a) ∈ R2 From (1) and (2) If (a, b) ∈ R1 ∩ R2, then (b, a) ∈ R1 ∩ R2 Hence , R1 ∩ R2 is symmetric. Checking transitive R1 is transitive, Hence, if (a, b) ∈ R1 & (b, c) ∈ R1 , then (a, c) ∈ R1 R2 is transitive, Hence, if (a, b) ∈ R2 & (b, c) ∈ R2 , then (a, c) ∈ R2 From (3) & (4) If (a, b) ∈ R1 ∩ R2 and (b, c) ∈ R1 ∩ R2 , then (a, c) ∈ R1 ∩ R2, ∴ R1∩ R2 is transitive. Thus, R1 ∩ R2 is an equivalence relation.