




Miscellaneous
Last updated at Dec. 16, 2024 by Teachoo






Transcript
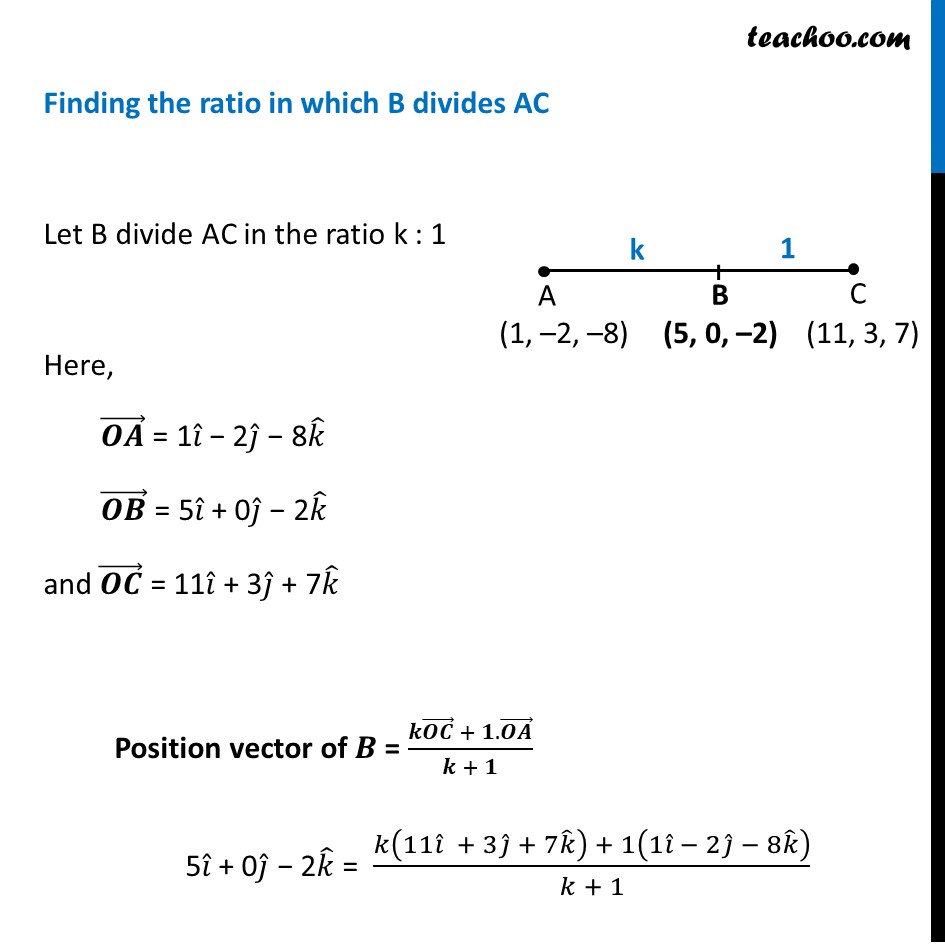
Misc 8 (Introduction) Show that the points A(1, – 2, – 8), B (5, 0, – 2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC. (1) Three points collinear i.e. AB + BC = AC (2) Three position vectors collinear i.e. |(𝐴𝐵) ⃗ | + |(𝐵𝐶) ⃗ | = |(𝐴𝐶) ⃗ | Misc 8 Show that the points A(1, – 2, – 8), B (5, 0, – 2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC. vGiven A (1, -2, −8) B (5, 0,−2) C (11, 3, 7) 3 points A, B, C are collinear if |(𝑨𝑩) ⃗ | + |(𝑩𝑪) ⃗ | = |(𝑨𝑪) ⃗ | Finding (𝑨𝑩) ⃗ , (𝑩𝑪) ⃗ , (𝑨𝑪) ⃗ (𝑨𝑩) ⃗ = (5 − 1) 𝑖 ̂ + (0 − (−2)) 𝑗 ̂ + (−2−(−8)) 𝑘 ̂ = 4𝑖 ̂ + 2𝑗 ̂ + 6𝑘 ̂ (𝑩𝑪) ⃗ = (11 − 5) 𝑖 ̂ + (3 − 0) 𝑗 ̂ + (7−(−2)) 𝑘 ̂ = 6𝒊 ̂ + 3𝒋 ̂ + 9𝒌 ̂ (𝑨𝑪) ⃗ = (11 − 1) 𝑖 ̂ + (3 − (−2)) 𝑗 ̂ + (7−(−8)) 𝑘 ̂ = 10𝒊 ̂ + 5𝒋 ̂ + 15𝒌 ̂ Magnitude of (𝐴𝐵) ⃗ = √(42+22+62) |(𝑨𝑩) ⃗ | = √(16+4+36) = √56 = √(4×14 ) = 2√𝟏𝟒 Magnitude of (𝐵𝐶) ⃗ = √(62+32+92) |(𝑩𝑪) ⃗ |= √(36+9+81) = √126 = √(9×14 ) = 3√𝟏𝟒 Magnitude of (𝐴𝐶) ⃗ = √(102+52+152) |(𝑨𝑪) ⃗ |= √(100+25+225)= √350 = √(25 × 14 ) = 5√𝟏𝟒 Thus, |(𝑨𝑩) ⃗ | + |(𝑩𝑪) ⃗ | = 2√(14 ) + 3√(14 ) = 5√(14 ) = |(𝑨𝑪) ⃗ | Thus, A, B and C are collinear. Finding the ratio in which B divides AC Let B divide AC in the ratio k : 1 Here, (𝑶𝑨) ⃗ = 1𝑖 ̂ − 2𝑗 ̂ − 8𝑘 ̂ (𝑶𝑩) ⃗ = 5𝑖 ̂ + 0𝑗 ̂ − 2𝑘 ̂ and (𝑶𝑪) ⃗ = 11𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 7𝑘 ̂ Position vector of 𝑩 = (𝒌(𝑶𝑪) ⃗ + 𝟏.(𝑶𝑨) ⃗)/(𝒌 + 𝟏) 5𝑖 ̂ + 0𝑗 ̂ − 2𝑘 ̂ = (𝑘(11𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑗 ̂ + 7𝑘 ̂ ) + 1(1𝑖 ̂ − 2𝑗 ̂ − 8𝑘 ̂ ))/(𝑘 + 1) 5𝑖 ̂ + 0𝑗 ̂ − 2𝑘 ̂ = (11𝑘𝑖 ̂ + 3𝑘𝑗 ̂ + 7𝑘 𝑘 ̂ + 𝑖 ̂ − 2𝑗 ̂ − 8𝑘 ̂)/(𝑘 + 1) 5𝒊 ̂ + 0𝒋 ̂ − 2𝒌 ̂ = ((𝟏𝟏𝒌 + 𝟏) 𝒊 ̂ + (𝟑𝒌 − 𝟐) 𝒋 ̂ + (𝟕𝒌 − 𝟖) 𝒌 ̂)/(𝒌 + 𝟏) Since the two vectors are equal, corresponding components are also equal. So, (𝟏𝟏𝒌 + 𝟏)/(𝒌 + 𝟏) = 5 11k + 1 = 5k + 5 11k – 5k = 5 − 1 6k = 4 k = 4/6 = 2/3 Thus, B divides AC in the ratio 2 : 3