

Chapter 8 Class 12 Application of Integrals
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo






Transcript
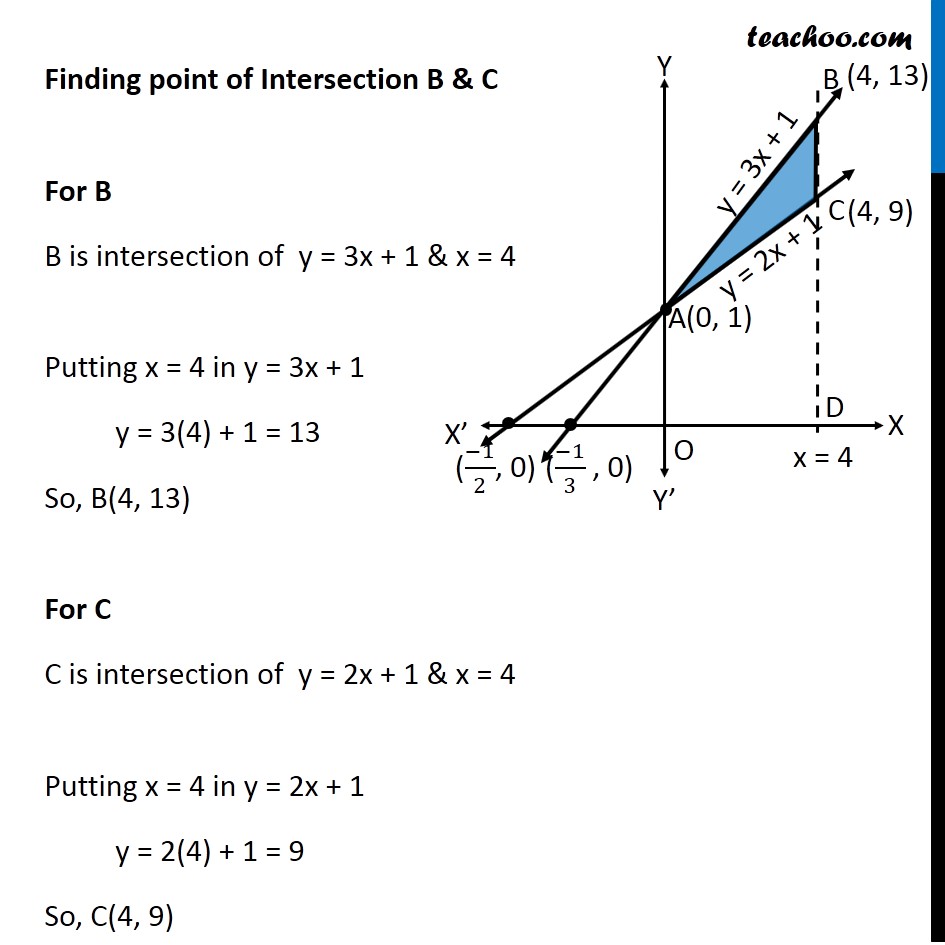
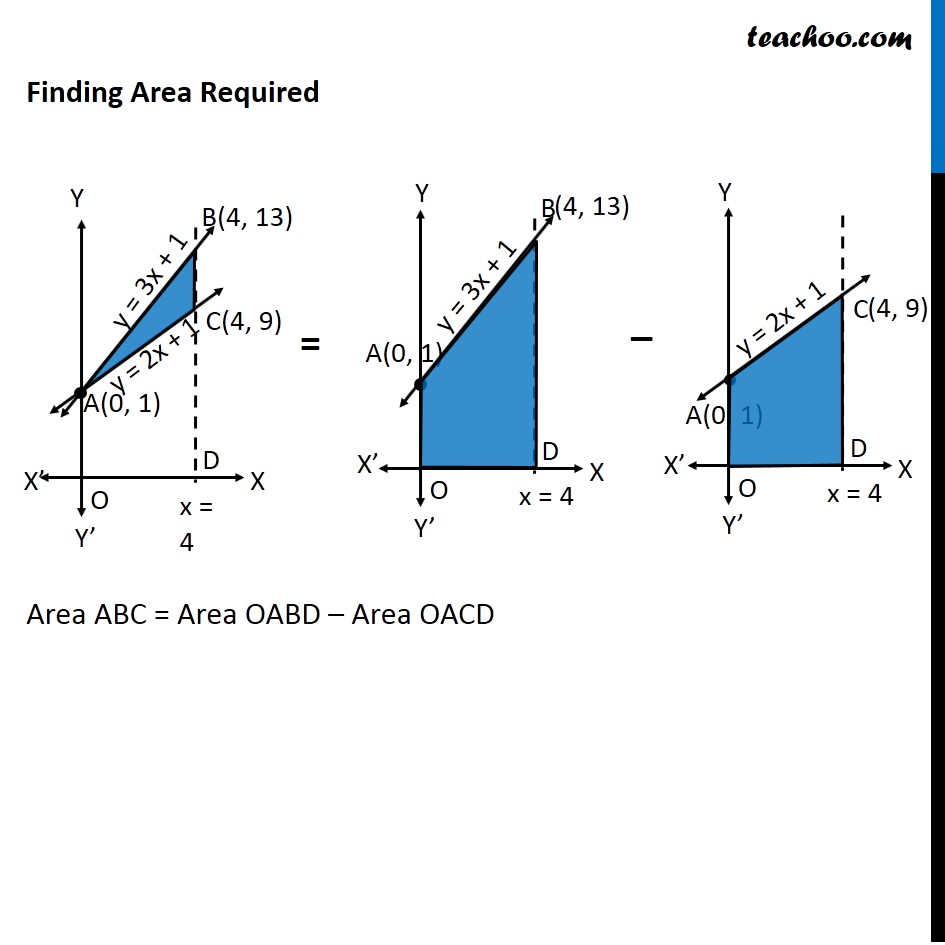
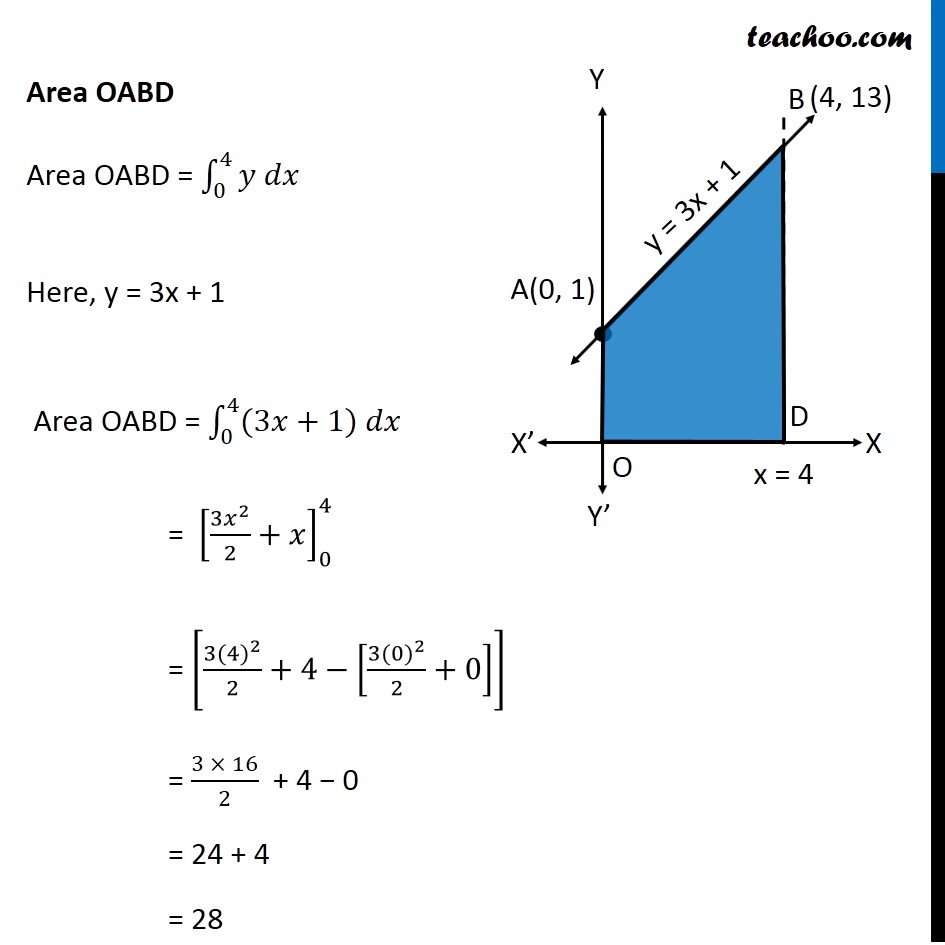
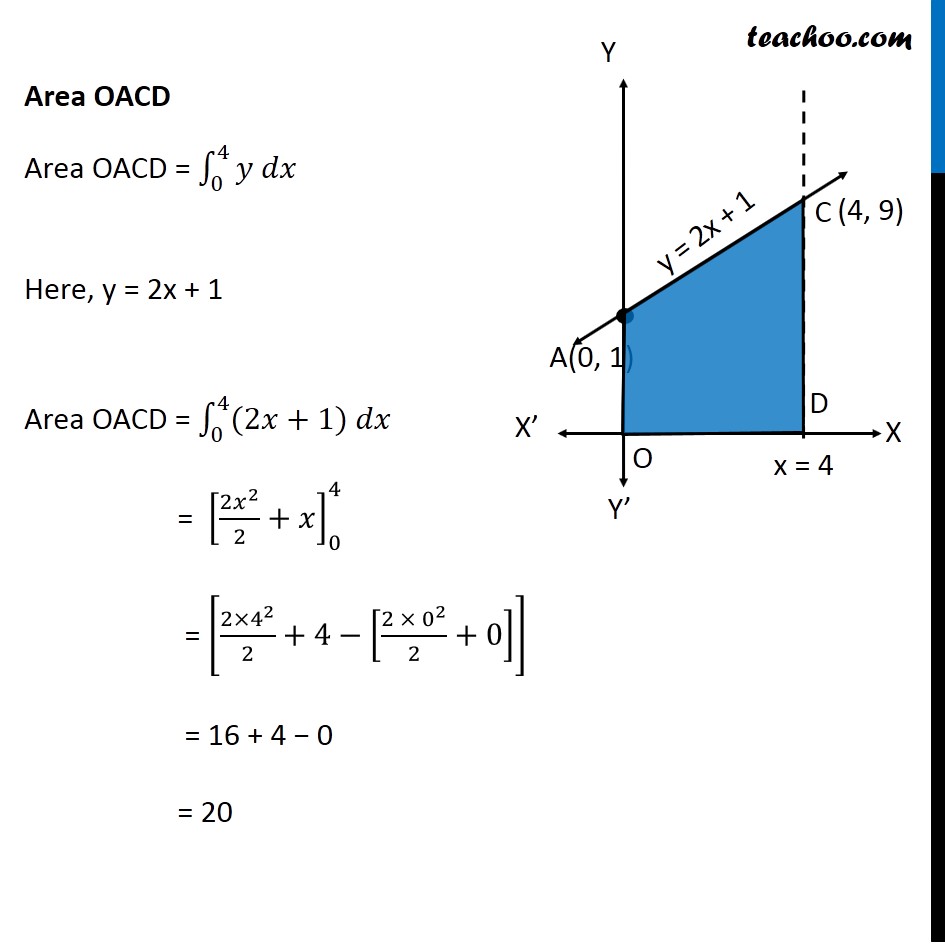
Ex 8.2 , 5 Using integration find the area of the triangular region whose sides have the equations 𝑦=2𝑥+1, 𝑦=3𝑥+1 and 𝑥=4 Lets Draw the figure & x = 4 Therefore, Required Area = Area ABC Finding point of Intersection B & C For B B is intersection of y = 3x + 1 & x = 4 Putting x = 4 in y = 3x + 1 y = 3(4) + 1 = 13 So, B(4, 13) For C C is intersection of y = 2x + 1 & x = 4 Putting x = 4 in y = 2x + 1 y = 2(4) + 1 = 9 So, C(4, 9) Finding Area Required Area ABC = Area OABD – Area OACD Area OABD Area OABD = ∫1_0^4▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 Here, y = 3x + 1 Area OABD = ∫1_0^4▒〖(3𝑥+1) 𝑑𝑥〗 = [(3𝑥^2)/2+𝑥]_0^4 = [(3〖(4)〗^2)/2+4−[(3〖(0)〗^2)/2+0]] = (3 × 16)/2 + 4 − 0 = 24 + 4 = 28 Area OACD Area OACD = ∫1_0^4▒〖𝑦 𝑑𝑥〗 Here, y = 2x + 1 Area OACD = ∫1_0^4▒〖(2𝑥+1) 𝑑𝑥〗 = [(2𝑥^2)/2+𝑥]_0^4 = [(2〖×4〗^2)/2+4−[(2〖 × 0〗^2)/2+0]] = 16 + 4 − 0 = 20 Area Required = Area ABDO − Area ACDO = 28 − 20 = 8 square unit