

Examples
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo






Transcript
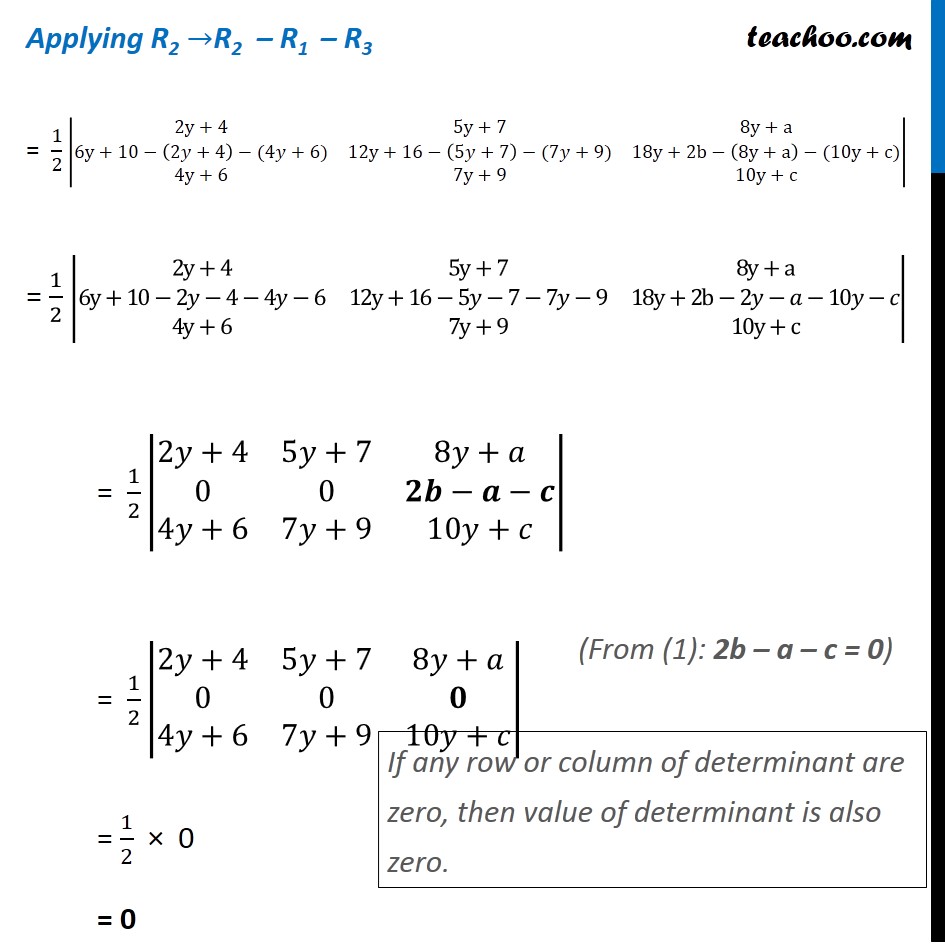
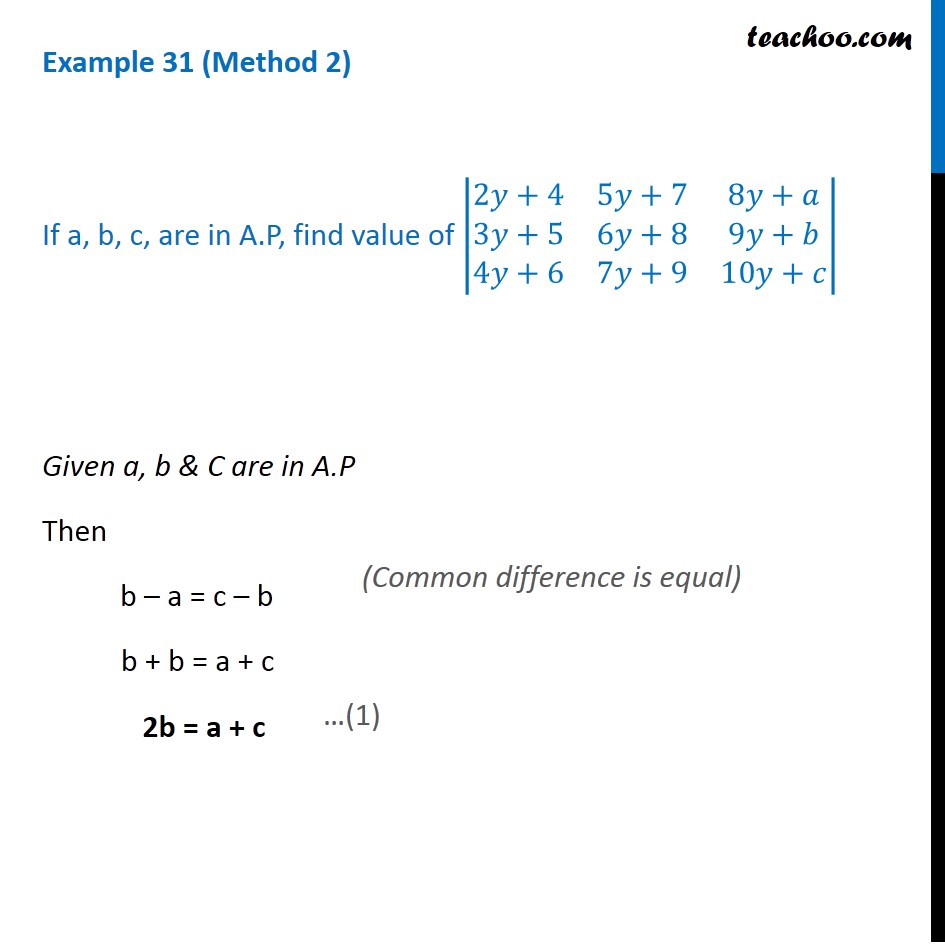
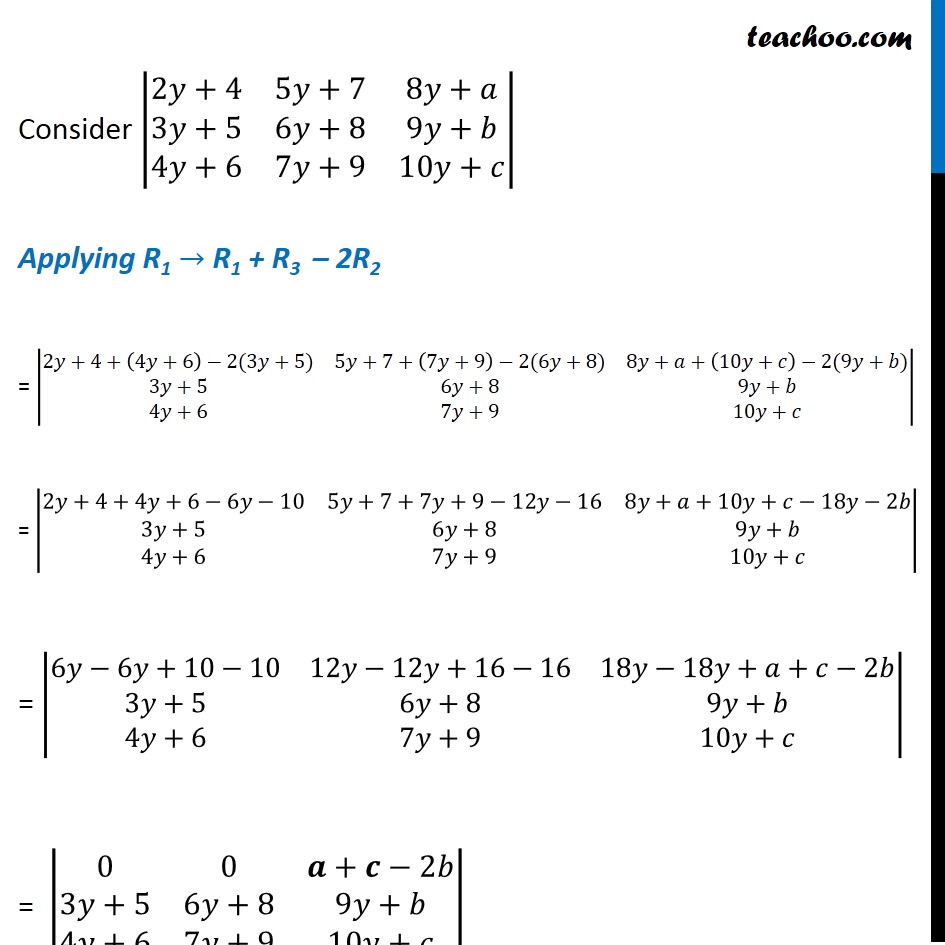
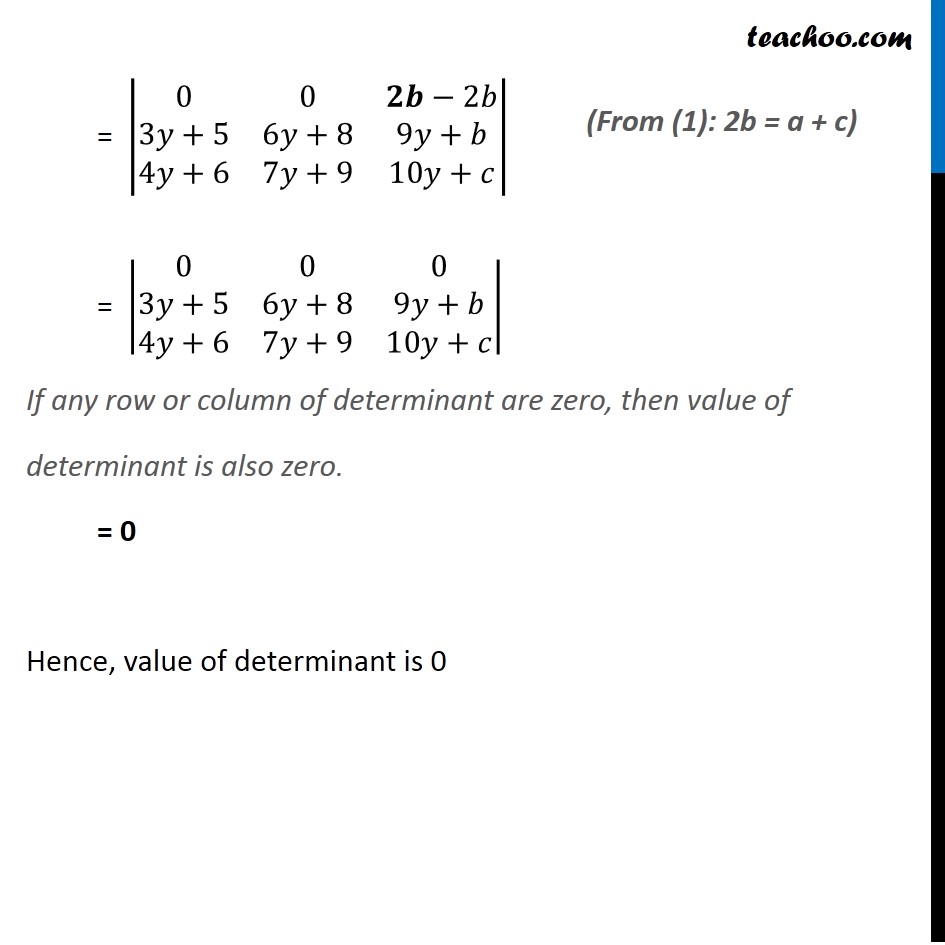
Question 13 (Method 1) If a, b, c, are in A.P, find value of |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@3y+5&6y+8&9y+b@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| Given a, b & c are in A.P Then, b – a = c – b b – a – c + b = 0 2b – a – c = 0 Solving (Common difference is equal) |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@3y+5&6y+8&9y+b@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| Multiply & Divide by 2 = 2/2 |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@3y+5&6y+8&9y+b@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| Multiplying 2 to R2 = 1/2 |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@𝟐(3y+5)&𝟐(6y+8)&𝟐(9y+b)@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| = 1/2 |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@6y+10&12y+16&18y+2b@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| Applying R2 →R2 – R1 – R3 = 1/2 |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@6y+10−(2𝑦+4)−(4𝑦+6)&12y+16−(5𝑦+7)−(7𝑦+9)&18y+2b−(8y+a)−(10y+c)@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| = 1/2 |■8(2y+4&5y+7&8y+a@6y+10−2𝑦−4−4𝑦−6&12y+16−5𝑦−7−7𝑦−9&18y+2b−2𝑦−𝑎−10𝑦−𝑐@4y+6&7y+9&10y+c)| = 1/2 |■8(2𝑦+4&5𝑦+7&8𝑦+𝑎@0&0&𝟐𝒃−𝒂−𝒄@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = 1/2 |■8(2𝑦+4&5𝑦+7&8𝑦+𝑎@0&0&𝟎@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = 1/2 × 0 = 0 Thus, the value of determinant is 0 (From (1): 2b – a – c = 0) If any row or column of determinant are zero, then value of determinant is also zero. Question 13 (Method 2) If a, b, c, are in A.P, find value of |■8(2𝑦+4&5𝑦+7&8𝑦+𝑎@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| Given a, b & C are in A.P Then b – a = c – b b + b = a + c 2b = a + c (Common difference is equal) Consider |■8(2𝑦+4&5𝑦+7&8𝑦+𝑎@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| Applying R1 → R1 + R3 – 2R2 = |■8(2𝑦+4+(4𝑦+6)−2(3𝑦+5)&5𝑦+7+(7𝑦+9)−2(6𝑦+8)&8𝑦+𝑎+(10𝑦+𝑐)−2(9𝑦+𝑏)@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = |■8(2𝑦+4+4𝑦+6−6𝑦−10&5𝑦+7+7𝑦+9−12𝑦−16&8𝑦+𝑎+10𝑦+𝑐−18𝑦−2𝑏@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = |■8(6𝑦−6𝑦+10−10&12𝑦−12𝑦+16−16&18𝑦−18𝑦+𝑎+𝑐−2𝑏@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = |■8(0&0&𝒂+𝒄−2𝑏@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = |■8(0&0&𝟐𝒃−2𝑏@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| = |■8(0&0&0@3𝑦+5&6𝑦+8&9𝑦+𝑏@4𝑦+6&7𝑦+9&10𝑦+𝑐)| If any row or column of determinant are zero, then value of determinant is also zero. = 0 Hence, value of determinant is 0 (From (1): 2b = a + c)