
Examples
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
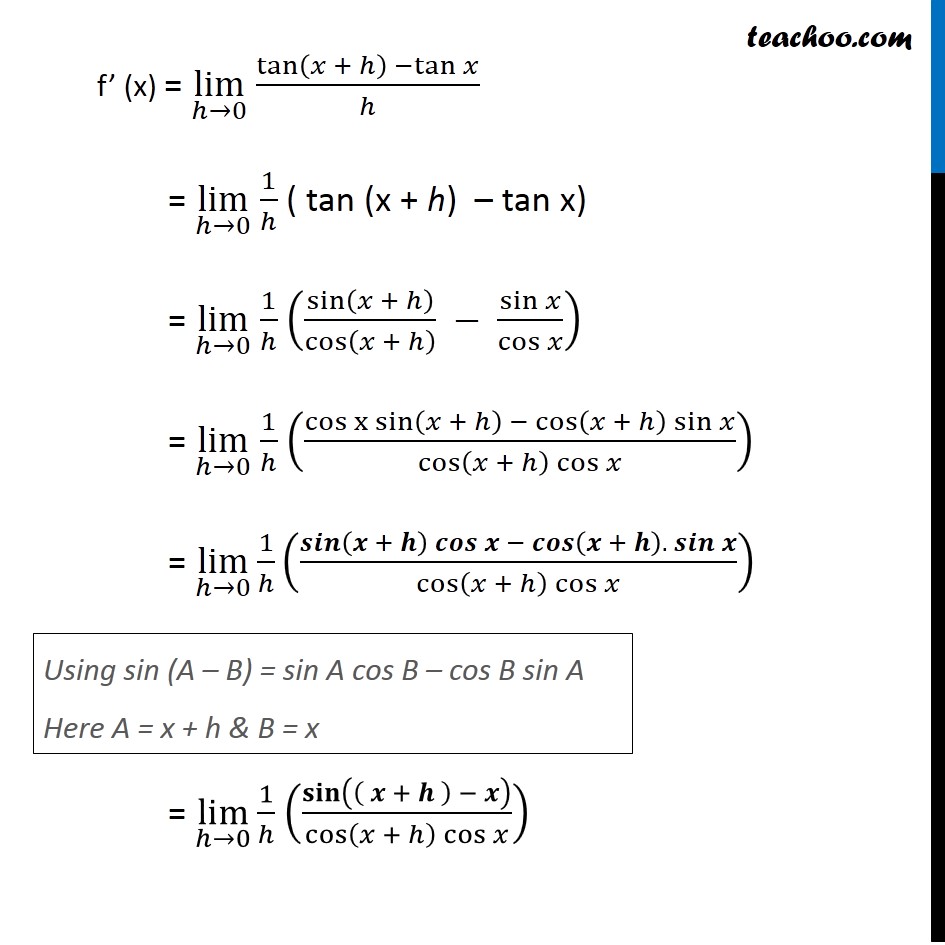
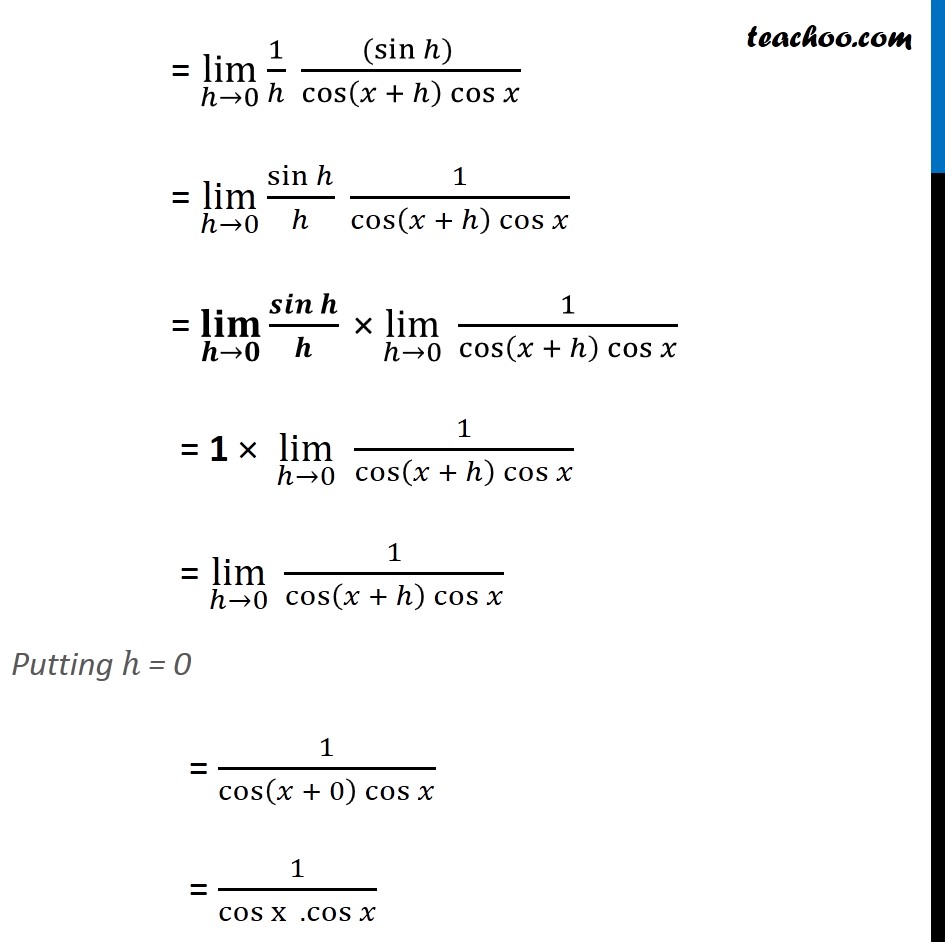
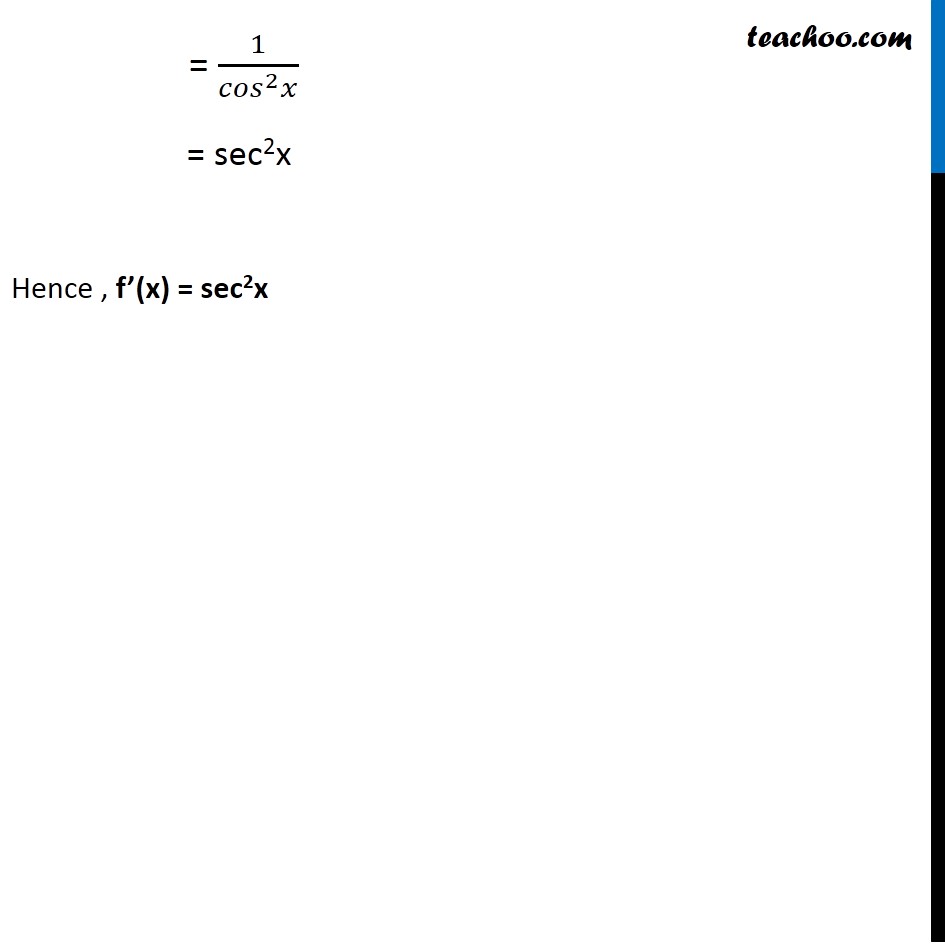
Example 17 Compute the derivative tan x. Let f(x) = tan x We need to find f’ (x) We know that f’(x) = lim┬(ℎ→0) f〖(𝑥 + ℎ) − f (x)〗/ℎ Here, f(x) = tan x f(x + ℎ) = tan (x + ℎ) Putting values f’ (x) = lim┬(ℎ→0) tan〖(𝑥 + ℎ) −tan𝑥 〗/ℎ = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ ( tan (x + h) – tan x) = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ (sin(𝑥 + ℎ)/cos(𝑥 + ℎ) − sin𝑥/cos𝑥 ) = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ (〖cos x sin〗〖(𝑥 + ℎ) −〖 cos〗〖(𝑥 + ℎ) sin𝑥 〗 〗/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 ) = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ (𝒔𝒊𝒏〖(𝒙 + 𝒉) 𝒄𝒐𝒔〖𝒙 − 𝒄𝒐𝒔〖(𝒙 + 𝒉). 〖 𝒔𝒊𝒏〗𝒙 〗 〗 〗/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 ) Using sin (A – B) = sin A cos B – cos B sin A Here A = x + h & B = x = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ (𝐬𝐢𝐧(( 𝒙 + 𝒉 ) − 𝒙)/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 ) = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/ℎ ((sin〖ℎ) 〗)/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 = lim┬(ℎ→0) sinℎ/ℎ 1/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 = (𝐥𝐢𝐦)┬(𝒉→𝟎) 𝒔𝒊𝒏𝒉/𝒉 " ×" lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 = 1 × lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 = lim┬(ℎ→0) 1/cos〖(𝑥 + ℎ) cos𝑥 〗 Putting ℎ = 0 = 1/cos〖(𝑥 + 0) cos𝑥 〗 = 1/〖cos x〗〖 .cos𝑥 〗 = 1/(〖𝑐𝑜𝑠〗^2 𝑥) = sec2x Hence , f’(x) = sec2x