
Area of combination of figures : sector based
Area of combination of figures : sector based
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
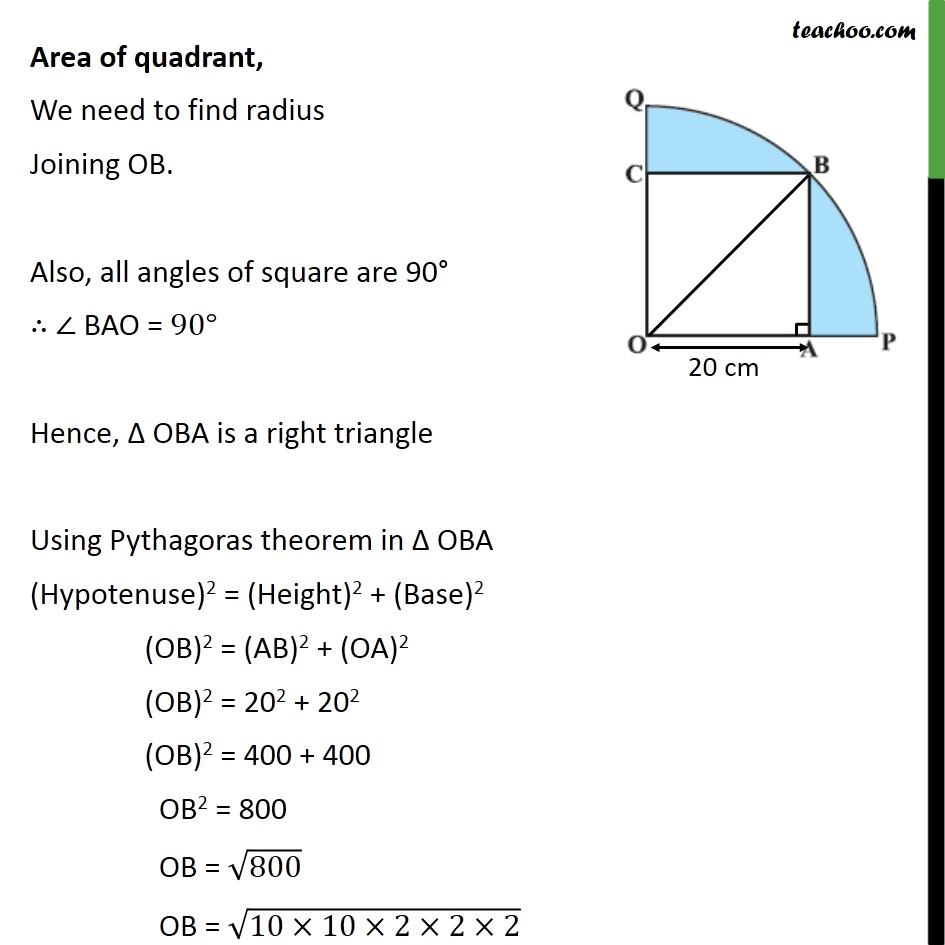
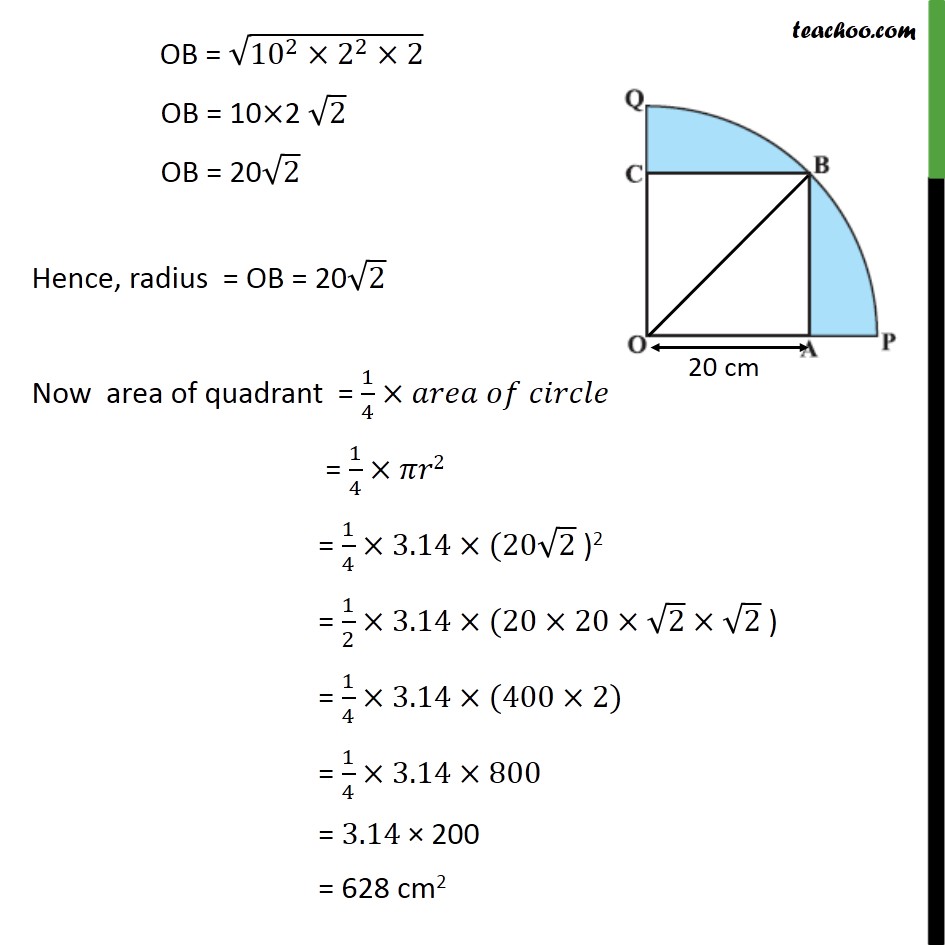
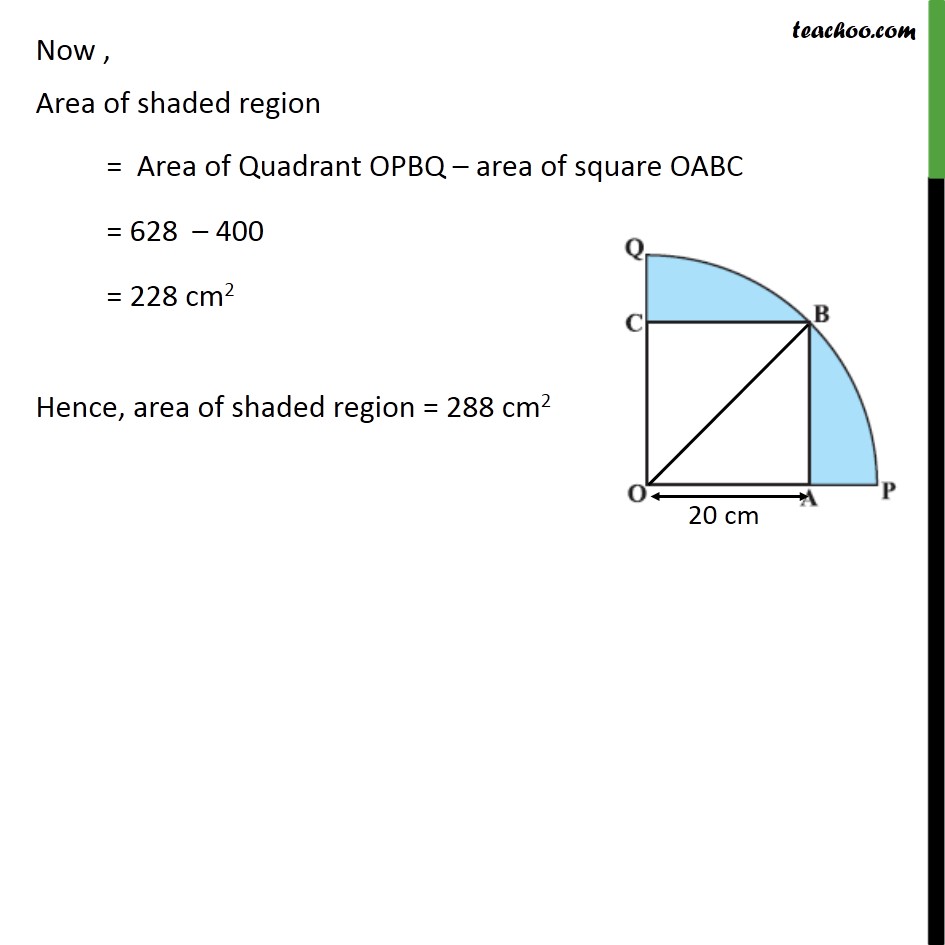
Question 13 In figure, a square OABC is inscribed in a quadrant OPBQ. If OA = 20 cm, find the area of the shaded region. (Use π= 3.14) Area of shaded region = Area of quadrant OPBQ – Area of square OABC Area of square Side of square = OA = 20 cm Area of square = (side)2 = (20)2 = 20×20 = 400 cm2 Area of quadrant, We need to find radius Joining OB. Also, all angles of square are 90° ∴ ∠ BAO = 90° Hence, Δ OBA is a right triangle Using Pythagoras theorem in Δ OBA (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 (OB)2 = (AB)2 + (OA)2 (OB)2 = 202 + 202 (OB)2 = 400 + 400 OB2 = 800 OB = √800 OB = √(10×10×2×2×2) OB = √(〖10〗^2×2^2×2) OB = 10×2 √2 OB = 20√2 Hence, radius = OB = 20√2 Now area of quadrant = 1/4×𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑖𝑟𝑐𝑙𝑒 = 1/4×𝜋𝑟2 = 1/4×3.14×(20√2 )2 = 1/2×3.14×(20×20×√2×√2 ) = 1/4×3.14×(400×2) = 1/4×3.14×800 = 3.14 × 200 = 628 cm2 Now , Area of shaded region = Area of Quadrant OPBQ – area of square OABC = 628 – 400 = 228 cm2 Hence, area of shaded region = 288 cm2