
Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo





Transcript
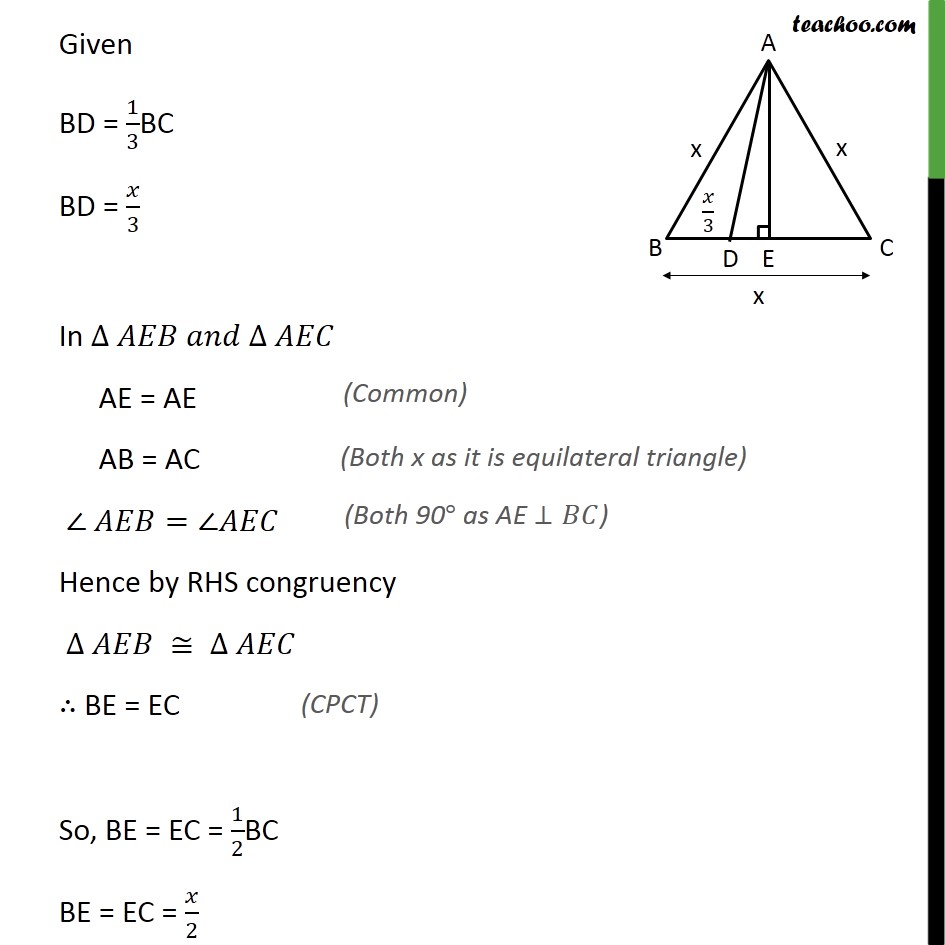
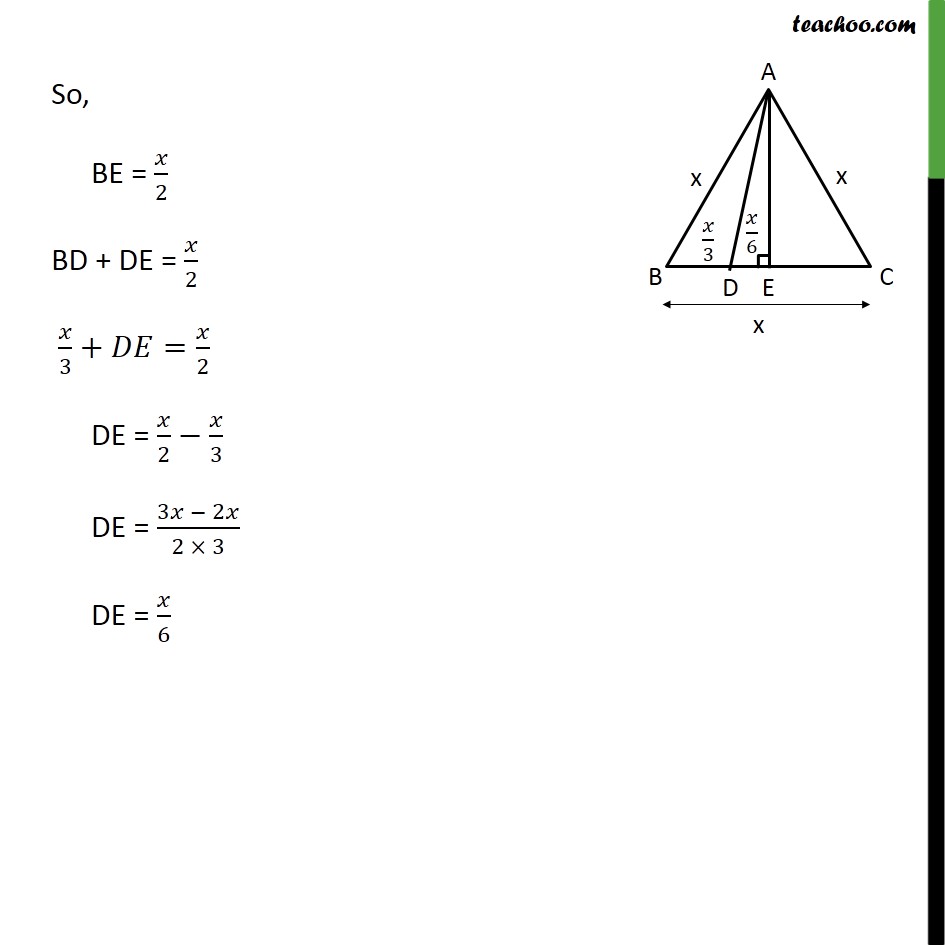
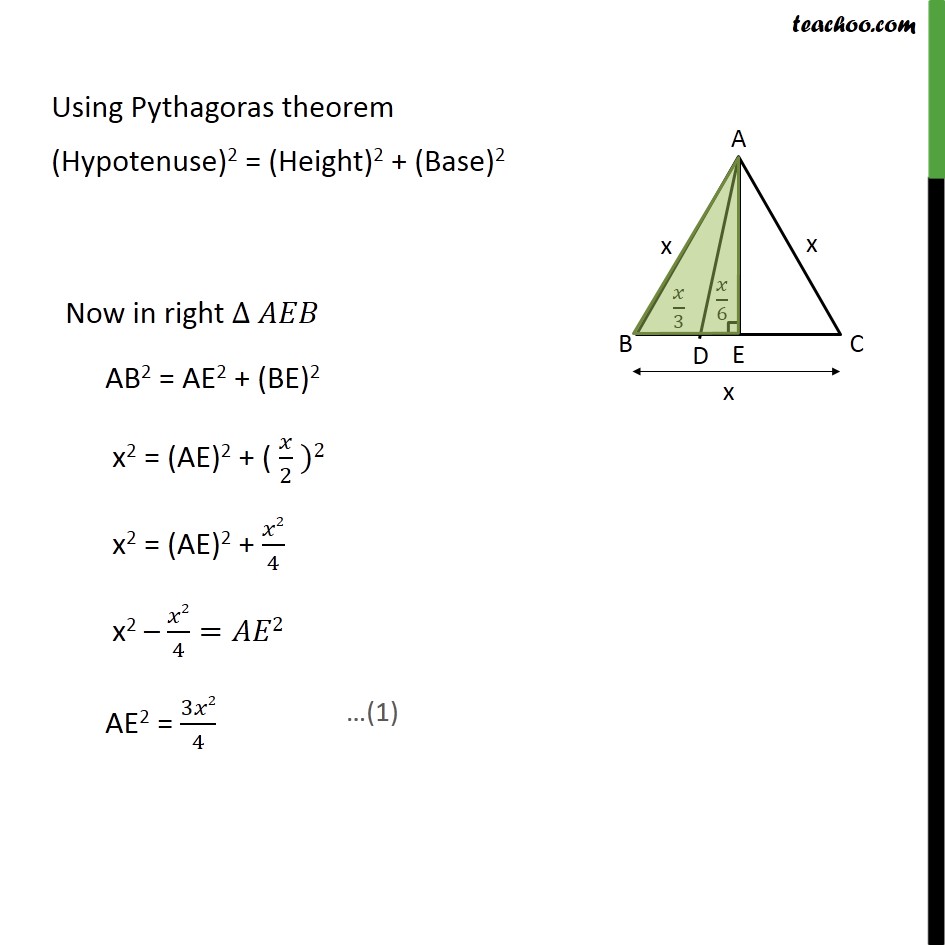
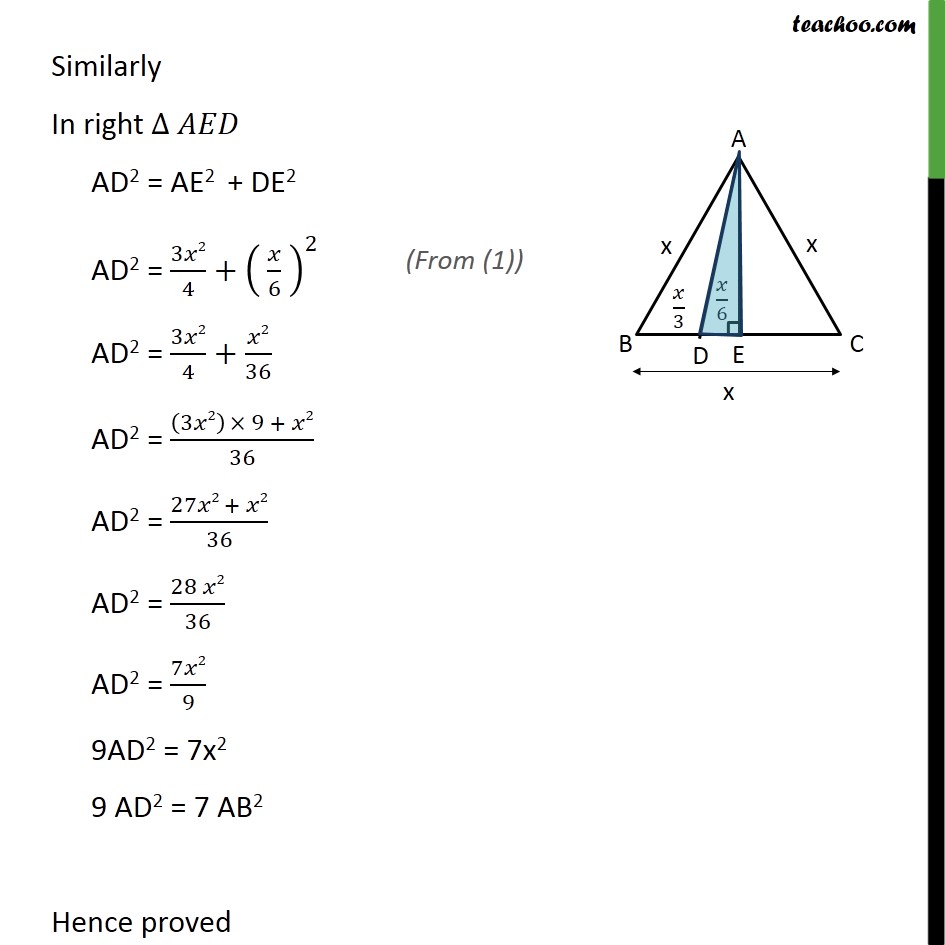
Question 15 In an equilateral triangle ABC, D is a point on side BC such that BD = 1/3BC. Prove that 9AD2 = 7 AB2 Given: Equilateral triangle ABC D is a point an BC Such that BD = 1/3 BC To prove: 9 AD2 = 7 AB2 Construction: Lets draw AE BC Proof: All sides of equilateral triangle is equal, AB = BC = AC Let AB = BC = AC = x Given BD = 1/3BC BD = /3 In AE = AE AB = AC = Hence by RHS congruency BE = EC So, BE = EC = 1/2BC BE = EC = /2 So, BE = /2 BD + DE = /2 /3+ = /2 DE = /2 /3 DE = (3 2 )/(2 3) DE = /6 Using Pythagoras theorem (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 Similarly In right AD2 = AE2 + DE2 AD2 = 3 2/4+( /6 )^2 AD2 = 3 2/4+ 2/36 AD2 = ((3 2) 9 + 2)/36 AD2 = (27 2 + 2)/36 AD2 = (28 2)/36 AD2 = 7 2/9 9AD2 = 7x2 9 AD2 = 7 AB2 Hence proved