
\

Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Chapter 6 Class 10 Triangles
Last updated at December 13, 2024 by Teachoo


\


Transcript
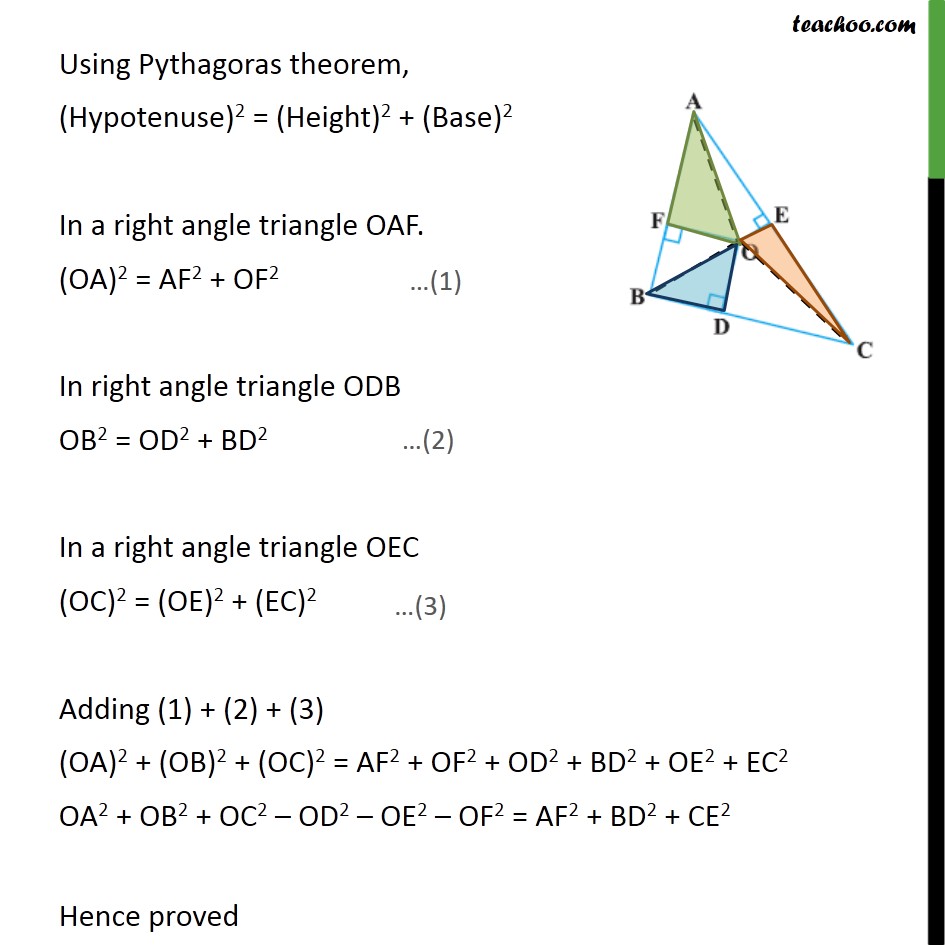
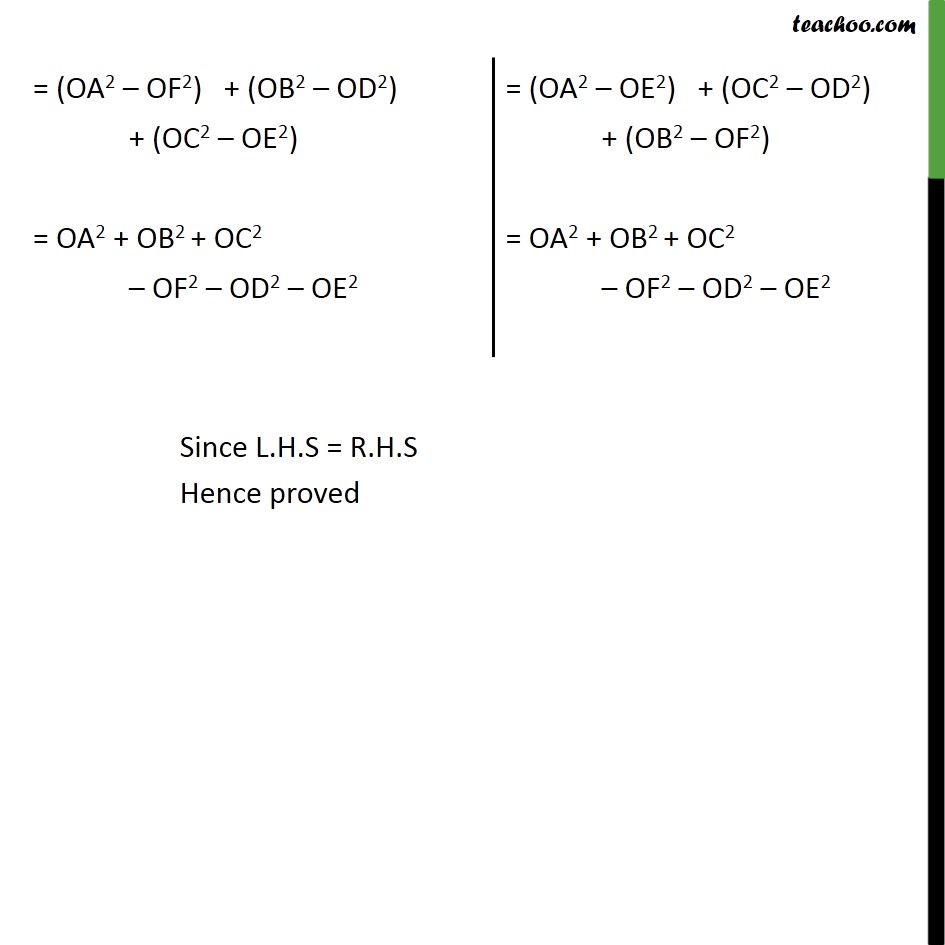
Question 8 In figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD ⊥BC, OE ⊥ AC and OF ⊥AB. Show that OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2 Given: Triangle ABC and O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC where, OD ⊥𝐵𝐶,𝑂𝐸⊥𝐴𝐶,𝑂𝐹⊥𝐴𝐵 To prove :- OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2 Proof:- Let us join the point O from A , B and C. Using Pythagoras theorem, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 In a right angle triangle OAF. (OA)2 = AF2 + OF2 In right angle triangle ODB OB2 = OD2 + BD2 In a right angle triangle OEC (OC)2 = (OE)2 + (EC)2 Adding (1) + (2) + (3) (OA)2 + (OB)2 + (OC)2 = AF2 + OF2 + OD2 + BD2 + OE2 + EC2 OA2 + OB2 + OC2 – OD2 – OE2 – OF2 = AF2 + BD2 + CE2 Hence proved Question8 In figure, O is a point in the interior of a triangle ABC, OD ⊥BC, OE ⊥AC and OF ⊥AB. Show that (ii) AF2 + BD2 + CE2 = AE2 + CD2 + BF2 Using Pythagoras theorem. (Hypotenuse)2 = (Height)2 + (Base)2 In Δ ODB, OB2 = OD2 + BD2 In Δ OFB, OB2 = OF2 + FB2 In Δ OFA, OA2 = OF2 + AF2 In Δ OEA, OA2 = OE2 + AE2 In Δ OEC, OC2 = OE2 + CE2 In Δ ODC, OC2 = OD2 + CD2