Find the shortest distance between the following lines
r ⃗ = (i ̂+j ̂-k ̂ )+s(2i ̂+j ̂+k ̂ )
r ⃗ = (i ̂+j ̂+k ̂ )+t(4i ̂+(2j) ̂+2k ̂ )
This question is similar to Example 12 - Chapter 11 Class 12 - Three Dimensional Geometry
![[Term 2 Class 12] Find the shortest distance between lines: r = (i+j-k - CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards (For Term 2)](https://cdn.teachoo.com/ae6d6585-d927-4ef3-b404-6cda494cd936/slide32.jpg)
CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards (For Term 2)
CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards (For Term 2)
Last updated at December 14, 2024 by Teachoo
This question is similar to Example 12 - Chapter 11 Class 12 - Three Dimensional Geometry
![[Term 2 Class 12] Find the shortest distance between lines: r = (i+j-k - CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards (For Term 2)](https://cdn.teachoo.com/ae6d6585-d927-4ef3-b404-6cda494cd936/slide32.jpg)



Transcript
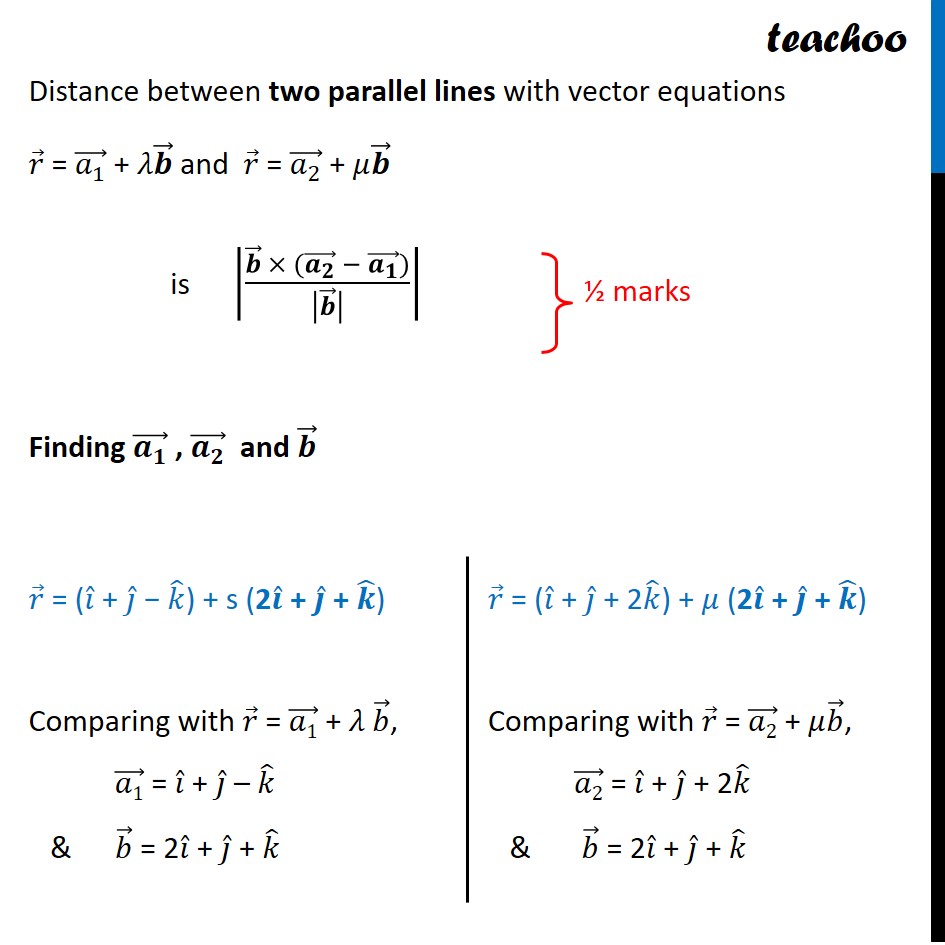
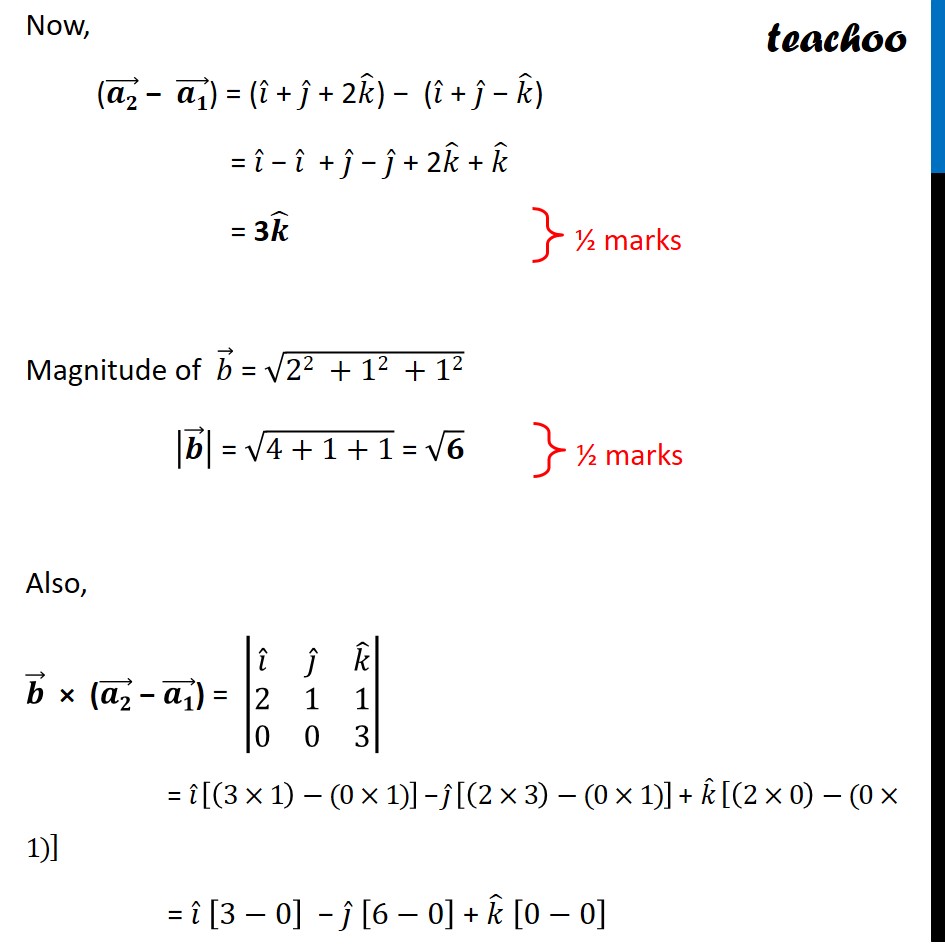
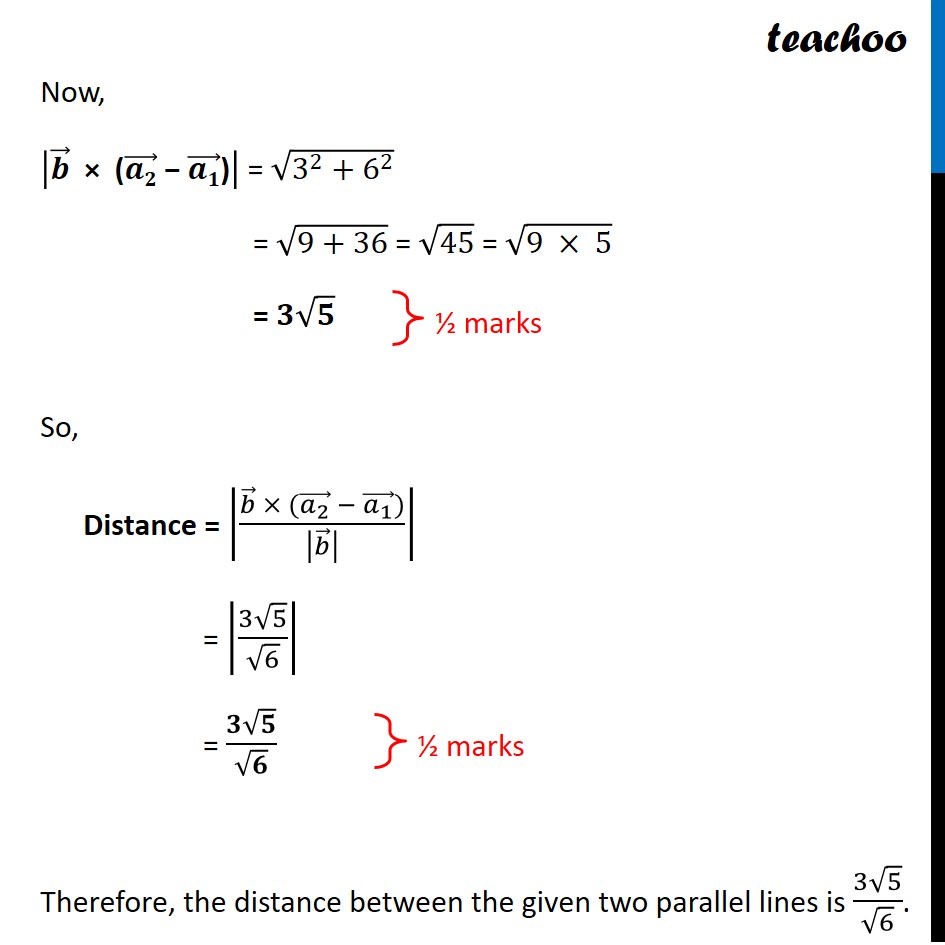
Question 10 (Choice 1) Find the shortest distance between the following lines: 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂−𝑘 ̂ )+𝑠(2𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂+𝑘 ̂ ) 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂+2𝑘 ̂ )+𝑡(4𝑖 ̂+2𝑗 ̂+2𝑘 ̂ ) Given lines 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂−𝑘 ̂ )+𝑠(2𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂+𝑘 ̂ ) 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂+2𝑘 ̂ )+𝑡(4𝑖 ̂+2𝑗 ̂+2𝑘 ̂ ) We can write them as 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂−𝑘 ̂ )+𝑠(𝟐𝒊 ̂+𝒋 ̂+𝒌 ̂ ) 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂+𝑗 ̂+2𝑘 ̂ )+2𝑡(𝟐𝒊 ̂+𝒋 ̂+𝒌 ̂ ) Since parallel vector is same, the lines are parallel Distance between two parallel lines with vector equations 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑎_1 ) ⃗ + 𝜆𝒃 ⃗ and 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑎_2 ) ⃗ + 𝜇𝒃 ⃗ is |(𝒃 ⃗ × ((𝒂_𝟐 ) ⃗ − (𝒂_𝟏 ) ⃗))/|𝒃 ⃗ | | Finding (𝒂_𝟏 ) ⃗ , (𝒂_𝟐 ) ⃗ and 𝒃 ⃗ 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ − 𝑘 ̂) + s (2𝒊 ̂ + 𝒋 ̂ + 𝒌 ̂) Comparing with 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑎1) ⃗ + 𝜆 𝑏 ⃗, (𝑎1) ⃗ = 𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ – 𝑘 ̂ & 𝑏 ⃗ = 2𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂ 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ + 2𝑘 ̂) + 𝜇 (2𝒊 ̂ + 𝒋 ̂ + 𝒌 ̂) Comparing with 𝑟 ⃗ = (𝑎2) ⃗ + 𝜇𝑏 ⃗, (𝑎2) ⃗ = 𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ + 2𝑘 ̂ & 𝑏 ⃗ = 2𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂ Now, ((𝒂𝟐) ⃗ − (𝒂𝟏) ⃗) = (𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ + 2𝑘 ̂) − (𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ − 𝑘 ̂) = 𝑖 ̂ − 𝑖 ̂ + 𝑗 ̂ − 𝑗 ̂ + 2𝑘 ̂ + 𝑘 ̂ = 3𝒌 ̂ Magnitude of 𝑏 ⃗ = √(22 +12 +12) |𝒃 ⃗ | = √(4+1+1) = √𝟔 Also, 𝒃 ⃗ × ((𝒂𝟐) ⃗ − (𝒂𝟏) ⃗) = |■8(𝑖 ̂&𝑗 ̂&𝑘 ̂@2&1&1@0&0&3)| = 𝑖 ̂ [(3×1)−(0×1)] − 𝑗 ̂ [(2×3)−(0×1)] + 𝑘 ̂ [(2×0)−(0×1)] = 𝑖 ̂ [3−0] − 𝑗 ̂ [6−0] + 𝑘 ̂ [0−0] = 𝟑𝒊 ̂ − 6𝒋 ̂Now, |𝒃 ⃗" × (" (𝒂𝟐) ⃗" − " (𝒂𝟏) ⃗")" | = √(3^2+6^2 ) = √(9+36) = √45 = √(9 × 5) = 𝟑√𝟓 So, Distance = |(𝑏 ⃗ × ((𝑎_2 ) ⃗ − (𝑎_1 ) ⃗))/|𝑏 ⃗ | | = |(3√5)/√6| = (𝟑√𝟓)/√𝟔 Therefore, the distance between the given two parallel lines is (3√5)/√6.