We have seen that,
Some metals react immediately and vigorously with reactants, while others react slowly , or when the reaction mixture is heated/catalysed. Some do not react at all.
Metals react based on their reactivity.
Reactivity is the tendency of chemical substances to form products by itself .
- Reactivity series is an arrangement of metals and non-metals based on their tendencies to react with certain tendencies.
- The elements are arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity .
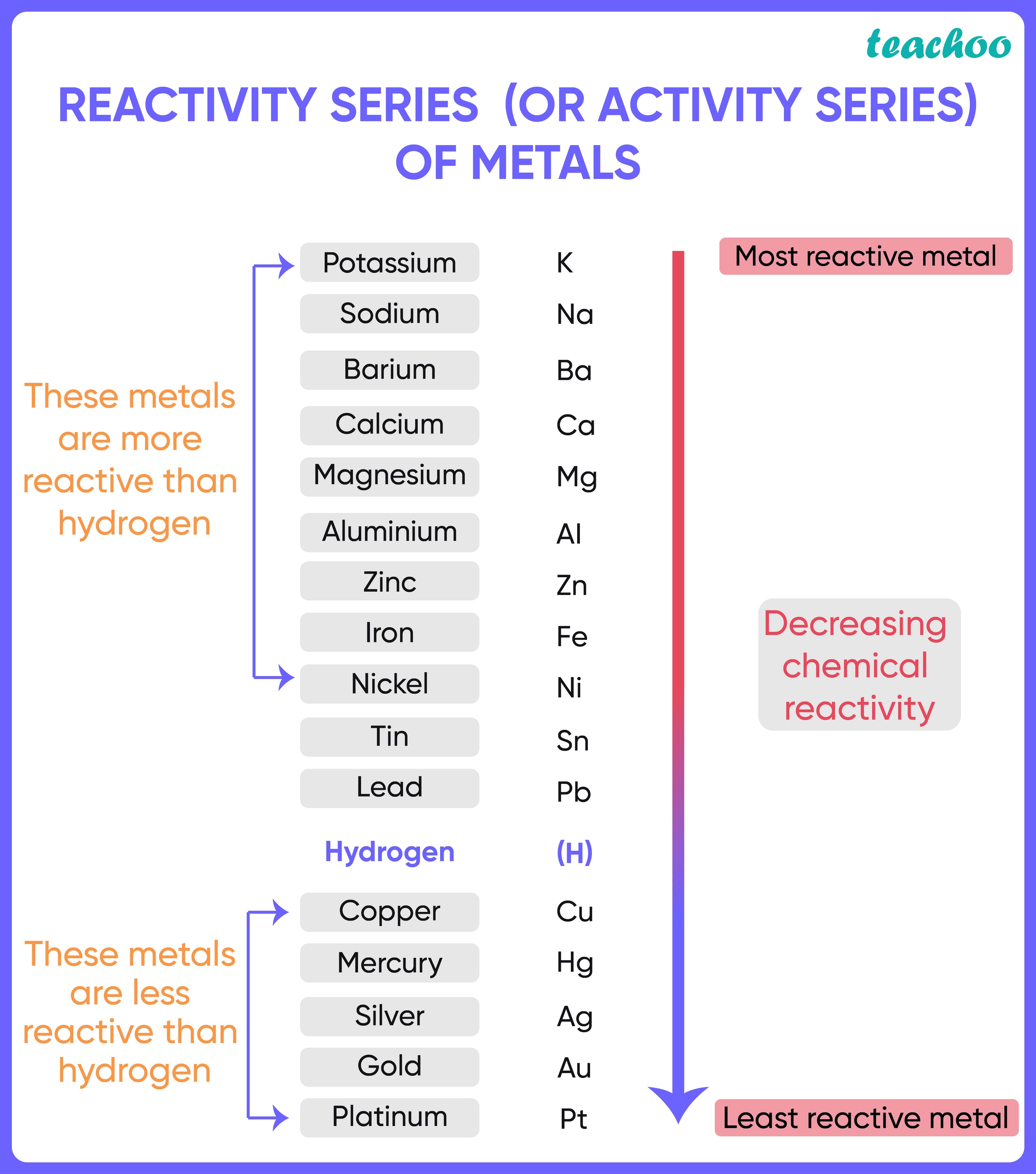
- The arrangement of metals in a vertical column in the degree of their decreasing reactivities (quality of being reactive) is called the reactivity series of metals.
- The most reactive metal is placed at the top whereas the least reactive metal is placed at the bottom .
Some common reactions of metals
- Sodium and Potassium can react vigorously with oxygen, water, and acids, as soon as they come into contact with them.
- On the other hand, heat is required for the reaction of magnesium with oxygen or air, or the reaction of magnesium with water.
- Thus, we can say that magnesium is less reactive than Sodium or Potassium.
- Similarly, we can say that Silver, Mercury, Gold, and Platinum are the least reactive metals as they rarely react with chemicals without external help.
Here's a list of Metal's reaction with Oxygen, Water, and common acids
|
Metal/Reactant |
Reaction with Oxygen |
Reaction with Water |
Reaction with HCl |
Reaction with H 2 SO 4 |
HNO 3 |
|
Potassium |
Reacts vigorously, catches fire |
Reacts vigorously with cold water, catches fire |
Reacts violently to form KCl |
Reacts violently to form K2SO4 |
Reacts violently to form KNO3 |
|
Sodium |
Reacts vigorously, catches fire |
Reacts vigorously with cold water, catches fire |
Reacts violently to form NaCl |
Reacts violently to form Na2SO4 |
Reacts violently to form NaNO3 |
|
Calcium |
Reacts with Oxygen to form oxide. Produces heat. |
Reacts with cold water, produces some heat |
Reacts rapidly to form CaCl |
Reacts rapidly to form CaSO4 |
Reacts rapidly to form Ca(NO3)2 |
|
Magnesium |
Requires external heat/combustion to react |
Requires external heat/hot water to react |
Reacts rapidly to form MgCl2 |
Reacts rapidly to form MgSO4 |
Reacts rapidly to form Mg(NO3)2 |
|
Aluminium |
Requires external heat/combustion to react |
Requires high amount external heat/steam to react |
Reacts slowly to form AlCl3 |
Reacts slowly to form Al2(SO4)3 |
Reacts slowly to form Al(NO3)3 |
|
Zinc |
Reacts only on strong heating |
Requires high amount external heat/steam to react |
Reacts slowly to form ZnCl2 |
Reacts slowly to form ZnSO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Zn(NO3)2 |
|
Iron |
Reacts only on strong heating/prolonged exposure |
Requires high amount external heat/steam to react |
Reacts very slowly to form FeCl2 |
Reacts slowly to form FeSO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Fe(NO3)3 |
|
Tin |
Reacts only on strong heating/prolonged exposure |
Reacts with steam to form SnO2+H2 |
Reacts very slowly to form SnCl4 |
Reacts slowly to form SnSO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Sn(NO3)4 |
|
Lead |
Reacts only on strong heating/prolonged exposure |
Reacts with steam to form PbO2+H2 |
Reacts very slowly to form PbCl4 |
Reacts slowly to form PbSO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Pb(NO3)2 |
|
Hydrogen |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Copper |
Reacts only on strong heating/prolonged exposure |
Does not react with Water |
Does not react with acid |
Reacts with hot, conc. acid to form CuSO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Cu(NO3)2 |
|
Mercury |
Does not react with Oxygen |
Does not react with Water |
Does not react with acid |
Reacts with hot, conc. acid to form Hg2SO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Hg2(NO3)2 |
|
Silver |
Does not react with Oxygen |
Does not react with Water |
Does not react with acid |
Reacts with hot, conc. acid to form Ag2SO4 |
Reacts slowly to form Ag(NO3) |
|
Gold |
Does not react with Oxygen |
Does not react with Water |
Does not react with acid |
Does not react with acid |
Does not react with acid |
|
Platinum |
Does not react with Oxygen |
Does not react with Water |
Does not react with acid |
Does not react with acid |
Does not react with acid |
Role of hydrogen in determining the reactivity series
In displacement reactions, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element.
- If a metal is above Hydrogen in the reactivity series, then it will displace hydrogen from water and acids, and hence produce hydrogen gas in the reaction.
- These lose electrons more readily than hydrogen, reactions with other substances are faster .
- Metals like Potassium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminium, Zinc, Iron, Tin and Lead are more reactive than hydrogen.
- Similarly, if a metal is below Hydrogen in the reactivity series, then it cannot displace hydrogen from water and acids, and thus, will not produce hydrogen gas upon reaction with water and acids.
- These lose electrons less readily than hydrogen, thus it reacts slowly with other substances.
- Metals like Gold, Silver, Copper and Mercury are less reactive than hydrogen and hence do not displace hydrogen from its salts/solutions.
Reaction of Metals with Other Metal Salts
What is a metal salt?
A metal salt is a compound formed when Hydrogen of an acid is replaced by a metal .
For Example :
In Zinc Sulphate, Zinc is a metal and Sulphuric Acid is an acid. Zinc reacts with sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas.

Zn (s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ---> ZnSO 4 (aq)+ H 2 (g)
This Zinc Sulphate is a Metal Salt , as it is formed by replacement of Hydrogen from H2SO 4 to form ZnSO 4 .
What is a Solution of Metal Salt?
- It is a mixture of Metal Salt in water .
- Example : Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO 4 ) is a metal salt. But Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO 4 ) (aq) is a solution of metal salt.

Displacement Reactions :
When a more reactive metal is placed in a salt solution of a less reactive metal, the more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt solution and forms a salt solution via displacement reaction.

Here, Metal A is more reactive than Metal B. Thus, it pushes metal B out of its salt solution.
For example : Zinc placed in Copper sulphate solution.
- We know that Zinc is more reactive than Copper (refer: reactivity series)
- When we put a piece of zinc metal in a copper sulphate solution,
- The zinc metal, being more reactive, displaces copper from the copper sulphate and forms zinc sulphate.
- This is called a displacement reaction.
- However if we put a piece of copper metal in a zinc sulphate solution, no displacement takes place
- This is because copper is less reactive than zinc.

