

Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo




Transcript
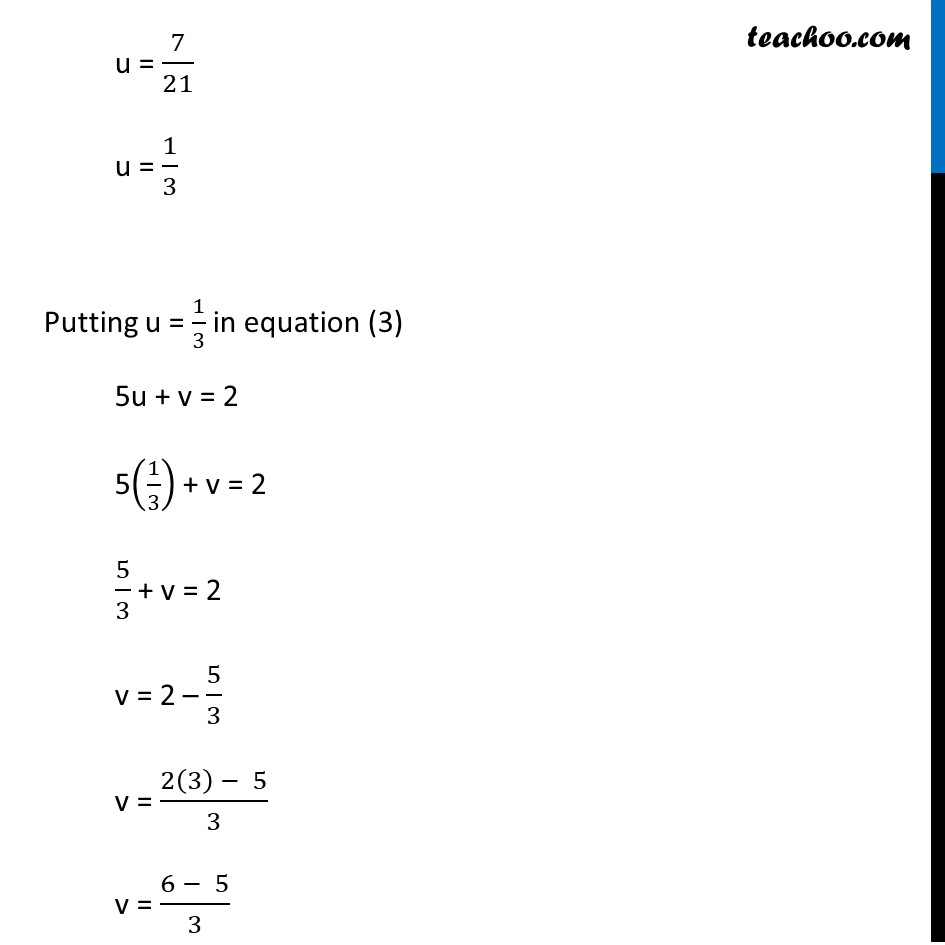
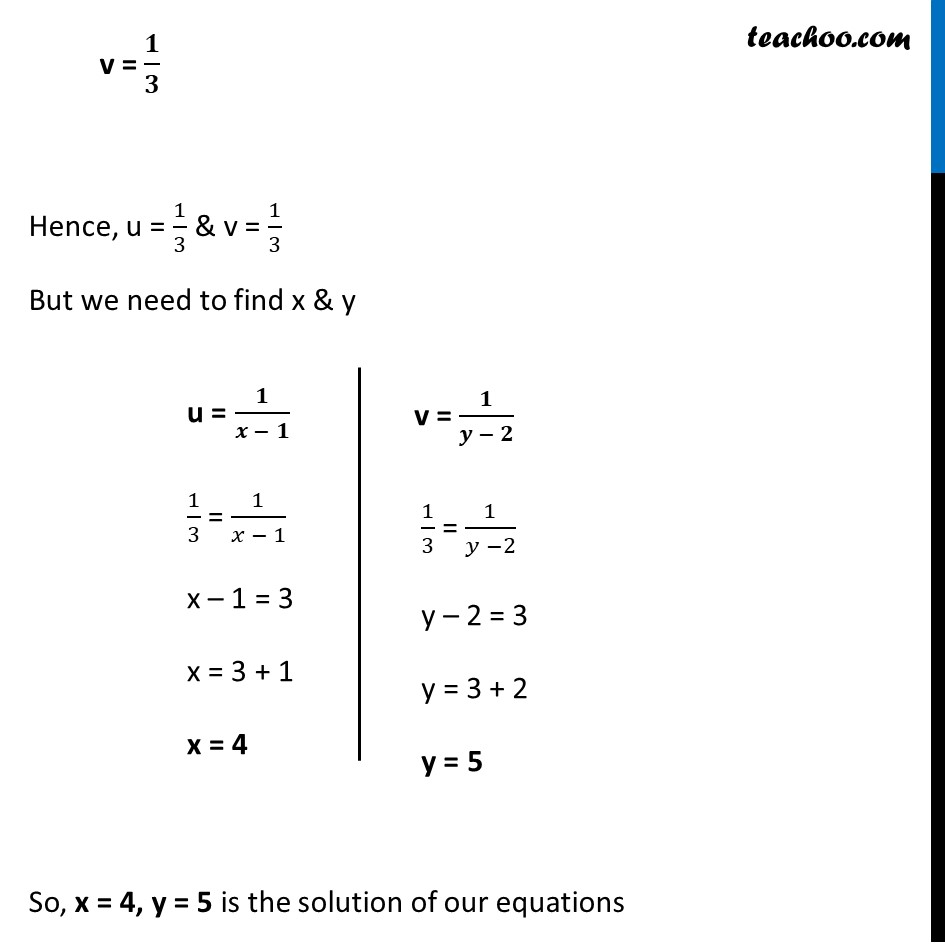
Question 8 Solve the following pair of equations by reducing them to a pair of linear equations : 5/(𝑥 −1) + 1/(𝑦 −2) = 2 6/(𝑥 −1) – 3/(𝑦 −2) = 1 5/(𝑥 − 1) + 1/(𝑦 − 2) = 2 6/(𝑥 − 1) – 3/(𝑦 − 2) = 1 So, our equations become 5u + v = 2 6u – 3v = 1 Thus, our equations are 5u + v = 2 …(3) 6u – 3v = 1 …(4) From (3) 5u + v = 2 v = 2 – 5u Putting value of v in (4) 6u – 3v = 1 6u – 3(2 – 5u) = 1 6u – 6 + 15u = 1 6u + 15u = 1 + 6 21u = 7 u = 7/21 u = 1/3 Putting u = 1/3 in equation (3) 5u + v = 2 5(1/3) + v = 2 5/3 + v = 2 v = 2 – 5/3 v = (2(3) − 5)/3 v = (6 − 5)/3 v = 𝟏/𝟑 Hence, u = 1/3 & v = 1/3 But we need to find x & y u = 𝟏/(𝒙 − 𝟏) 1/3 = 1/(𝑥 − 1) x – 1 = 3 x = 3 + 1 x = 4 v = 𝟏/(𝒚 − 𝟐) 1/3 = 1/(𝑦 −2) y – 2 = 3 y = 3 + 2 y = 5 So, x = 4, y = 5 is the solution of our equations