Let f: A → B be a function defined as f(x) = (2x + 3)/(x - 3) , where
A = R − {3} and B = R − {2}. Is the function f one–one and onto? Is f invertible? If yes, then find its inverse

CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2020 Boards
CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper for 2020 Boards
Last updated at December 16, 2024 by Teachoo






Transcript
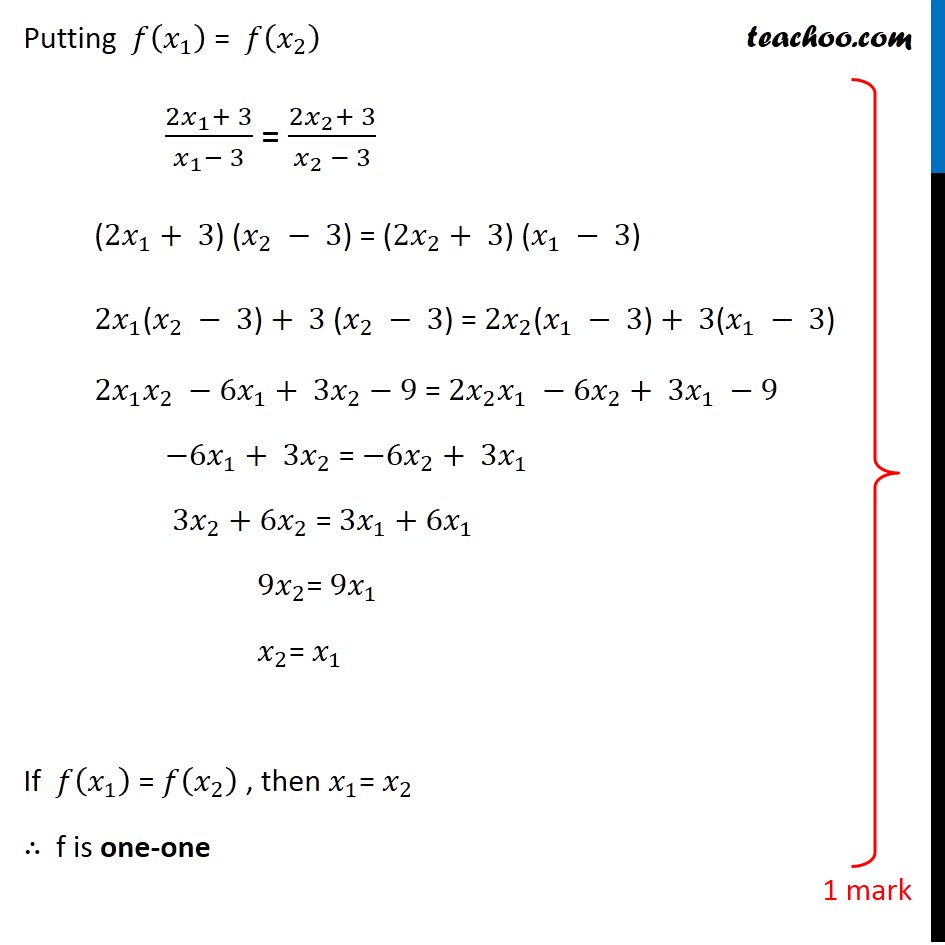
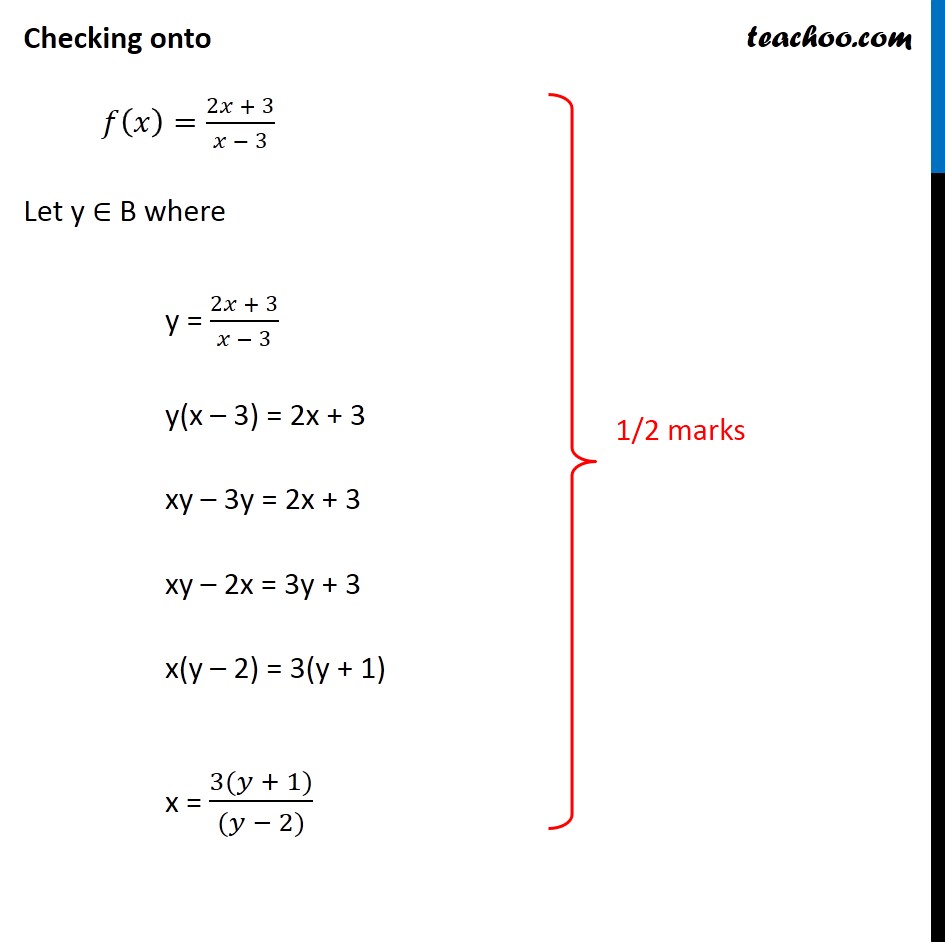
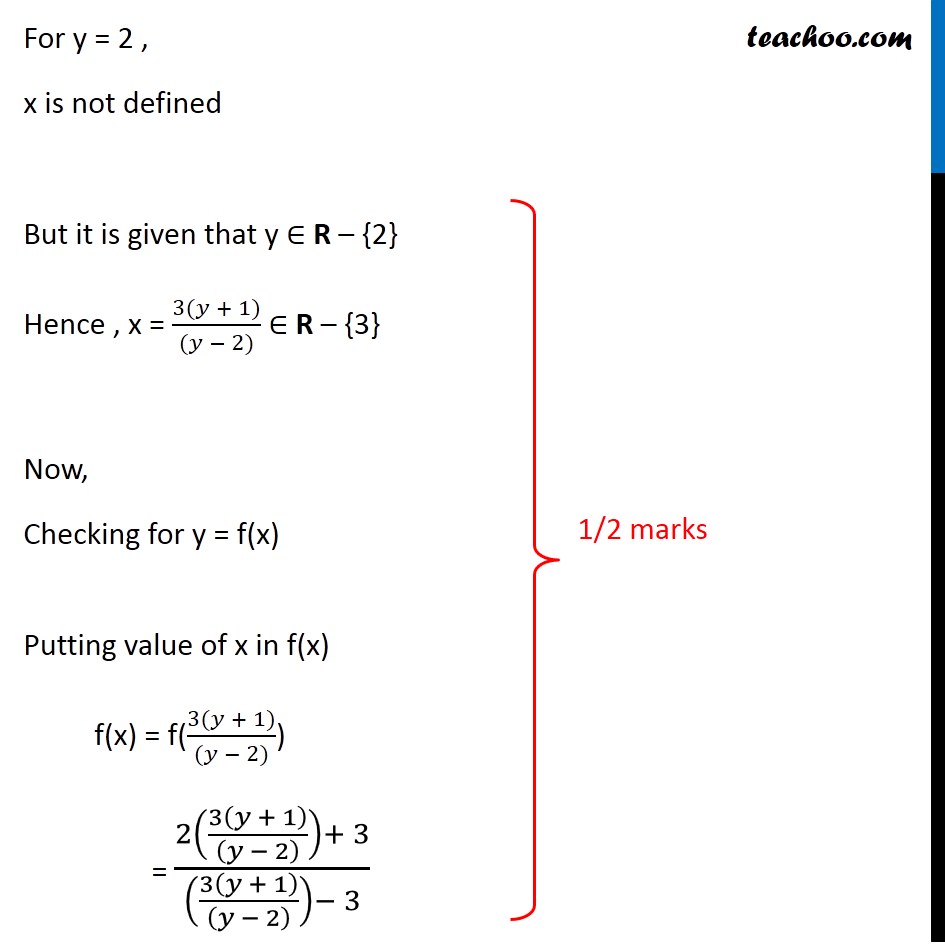
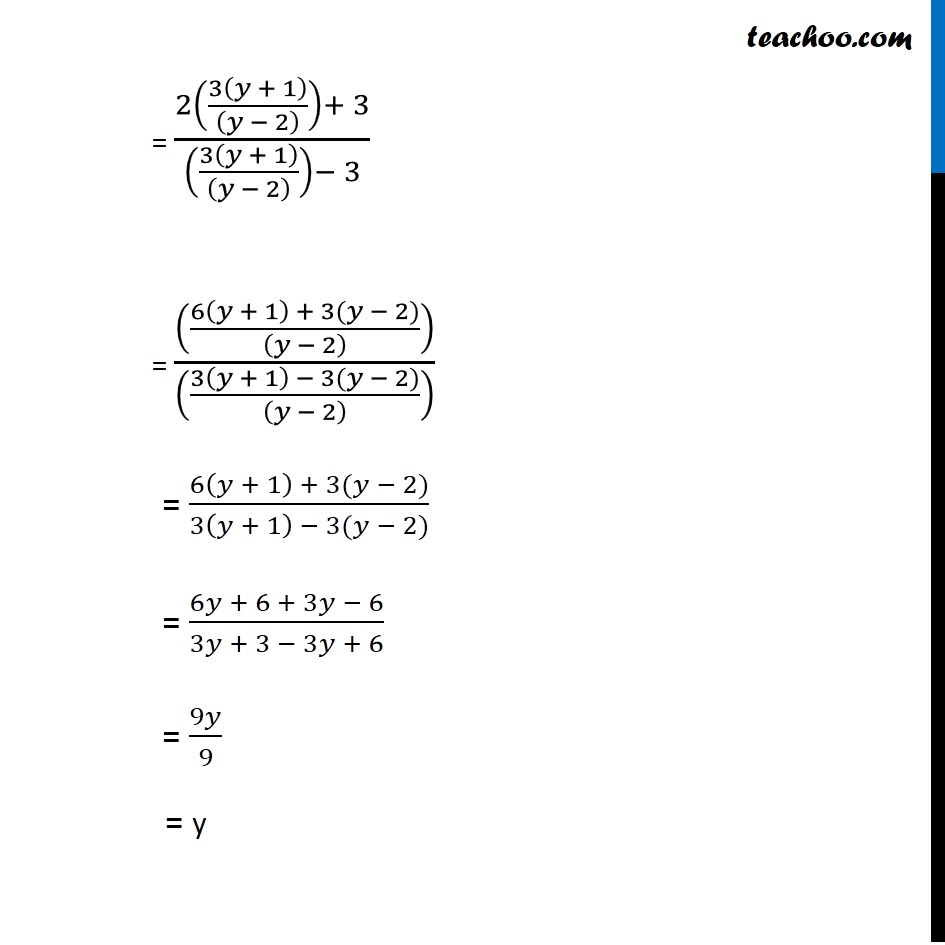
Question 27 Let 𝑓: A → B be a function defined as 𝑓(𝑥)=(2𝑥 + 3)/(𝑥 − 3) , where A = R − {3} and B = R − {2}. Is the function f one–one and onto? Is f invertible? If yes, then find its inverse 𝑓(𝑥)=(2𝑥 + 3)/(𝑥 − 3) Checking one-one Let 𝑥_1 , 𝑥_2 ∈ A 𝑓(𝑥_1 )=(2𝑥_1+ 3)/(𝑥_1− 3) 𝑓(𝑥_2 )=(2𝑥_2+ 3)/(𝑥_2 − 3) One-one Steps 1. Calculate f(x1) 2. Calculate f(x2) 3. Putting f(x1) = f(x2) we have to prove x1 = x2 Putting 𝑓(𝑥_1 ) = 𝑓(𝑥_2 ) (2𝑥_1+ 3)/(𝑥_1− 3) = (2𝑥_2+ 3)/(𝑥_2 − 3) (2𝑥_1+ 3) (𝑥_2 − 3) = (2𝑥_2+ 3) (𝑥_1 − 3) 2𝑥_1 "(" 𝑥_2 − 3")"+ 3 (𝑥_2 − 3) = 2𝑥_2 "(" 𝑥_1 − 3")"+ 3(𝑥_1 − 3) 2𝑥_1 𝑥_2 −6𝑥_1+ 3𝑥_2−9 = 2𝑥_2 𝑥_1 −6𝑥_2+ 3𝑥_1 −9 −6𝑥_1+ 3𝑥_2 = −6𝑥_2+ 3𝑥_1 3𝑥_2+6𝑥_2 = 3𝑥_1+6𝑥_1 9𝑥_2= 9𝑥_1 𝑥_2= 𝑥_1 If 𝑓(𝑥_1 ) = 𝑓(𝑥_2 ) , then 𝑥_1= 𝑥_2 ∴ f is one-one Checking onto 𝑓(𝑥)=(2𝑥 + 3)/(𝑥 − 3) Let y ∈ B where y = (2𝑥 + 3)/(𝑥 − 3) y(x – 3) = 2x + 3 xy – 3y = 2x + 3 xy – 2x = 3y + 3 x(y – 2) = 3(y + 1) x = (3(𝑦 + 1))/((𝑦 − 2)) For y = 2 , x is not defined But it is given that y ∈ R – {2} Hence , x = (3(𝑦 + 1))/((𝑦 − 2)) ∈ R – {3} Now, Checking for y = f(x) Putting value of x in f(x) f(x) = f((3(𝑦 + 1))/((𝑦 − 2))) = (2(3(𝑦 + 1)/((𝑦 − 2) ))+ 3)/((3(𝑦 + 1)/((𝑦 − 2) ))− 3) = (((6(𝑦 + 1)+3(𝑦−2))/((𝑦 − 2) )))/((3(𝑦 + 1)/((𝑦 − 2) ))− 3) Also, y = f(x) Putting y in f(x) Hence, f is onto = (2(3(𝑦 + 1)/((𝑦 − 2) ))+ 3)/((3(𝑦 + 1)/((𝑦 − 2) ))− 3) = (((6(𝑦 + 1) + 3(𝑦 − 2))/((𝑦 − 2) )))/(((3(𝑦 + 1) − 3(𝑦 − 2))/((𝑦 − 2) )) ) = (6(𝑦 + 1) + 3(𝑦 − 2))/(3(𝑦 + 1) − 3(𝑦 − 2)) = (6𝑦 + 6 + 3𝑦 − 6)/(3𝑦 + 3 − 3𝑦 + 6) = 9𝑦/9 = y Thus, for every y ∈ B, there exists x ∈ A such that f(x) = y Hence, f is onto Since f(x) is one-one and onto, So, f(x) is invertible And Inverse of x = 𝑓^(−1) (𝑦) = (3(𝑦 + 1))/((𝑦 − 2))