There are some rules which we use to obtain images in a ray diagram
Let's look at them
Rule 1 - Ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus after reflection
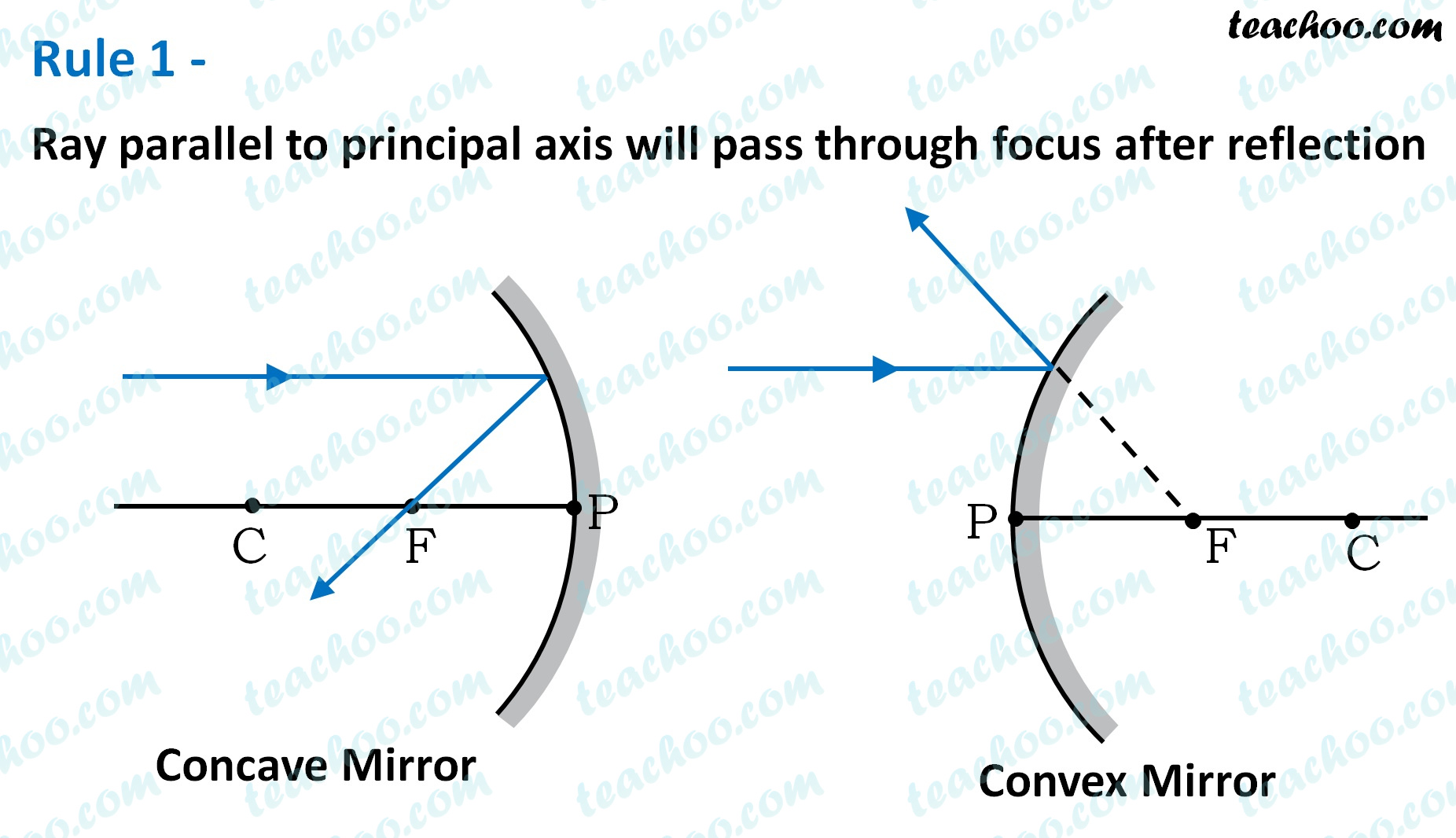
For a concave mirror,
we see that ray passes through focus after reflection
For a convex mirror ,
since focus is on the right side,
it appears that ray passes through focus after reflection
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis after reflection
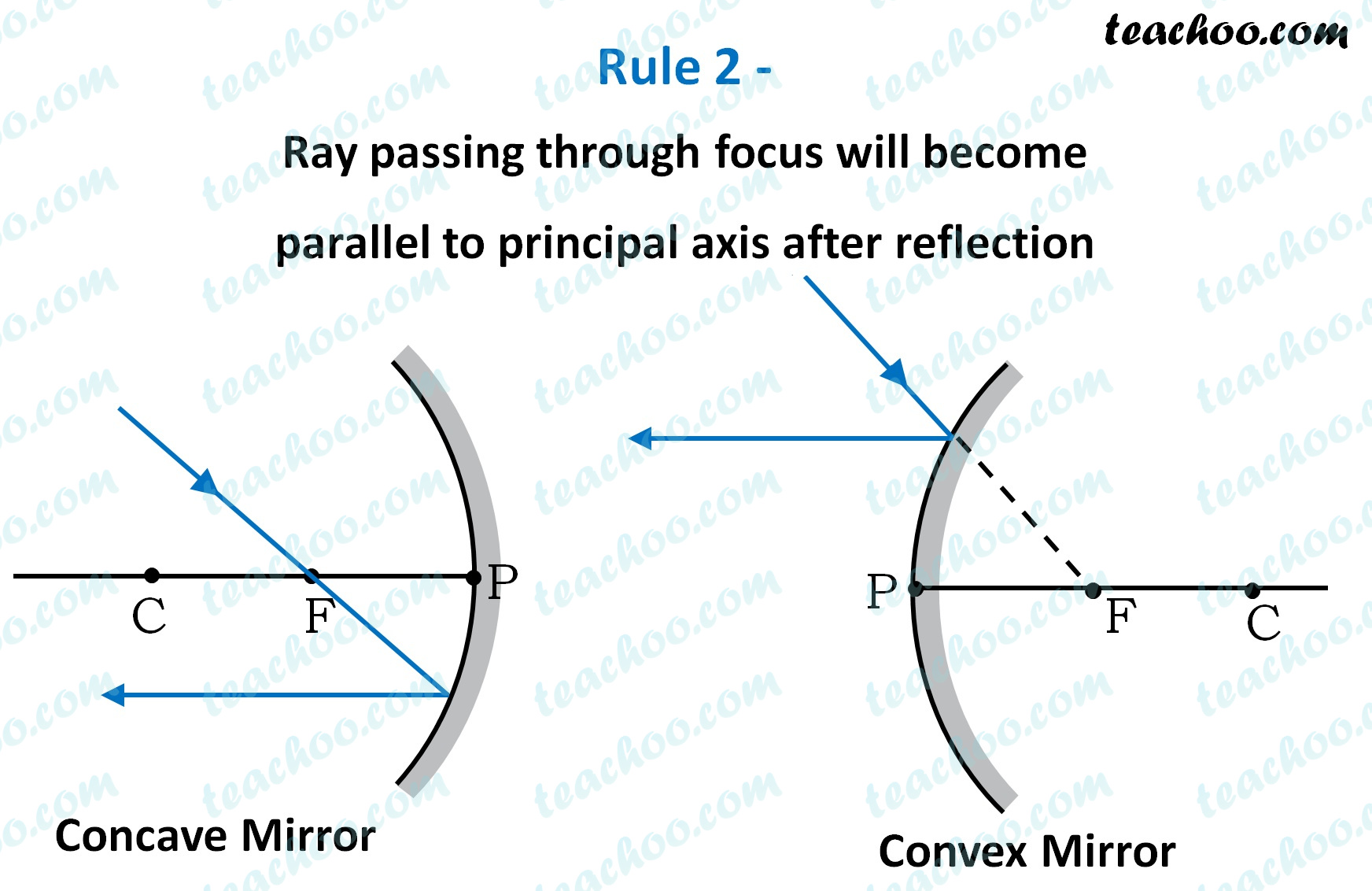
For a concave mirror ,
we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection
For a convex mirror,
since focus is on the right side,
it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis
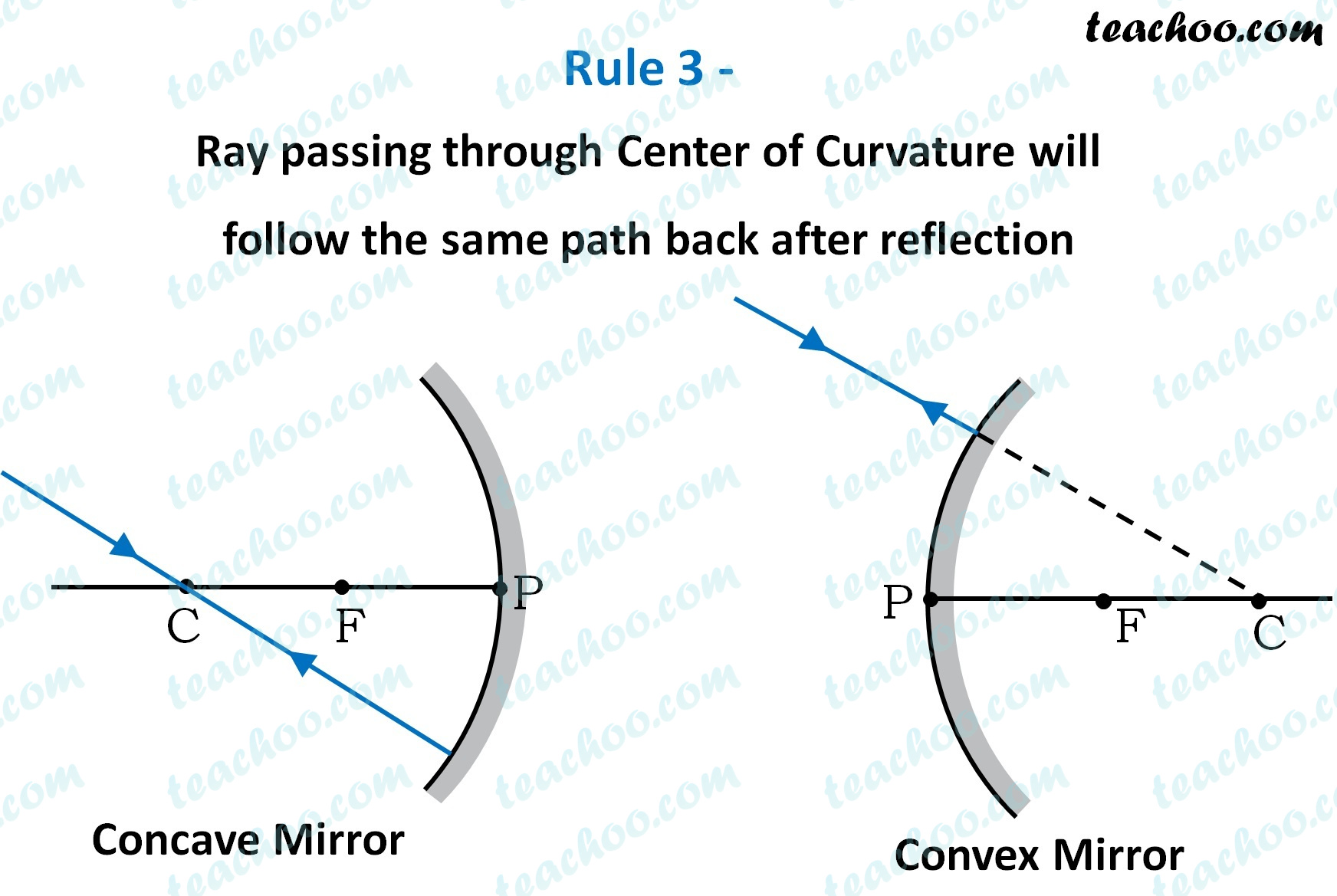
Rule 3 - Ray passing through Center of Curvature will follow the same path back after reflection
For a concave mirror ,
we see that ray passing through Centre of Curvature comes back the same path
For a convex mirror ,
since Center of Curvature is on the right side,
it appears that ray passes through Center of Curvature, and then it comes back along the same path
Rule 4 - Ray incident at pole is reflected back making same angle with principal axis
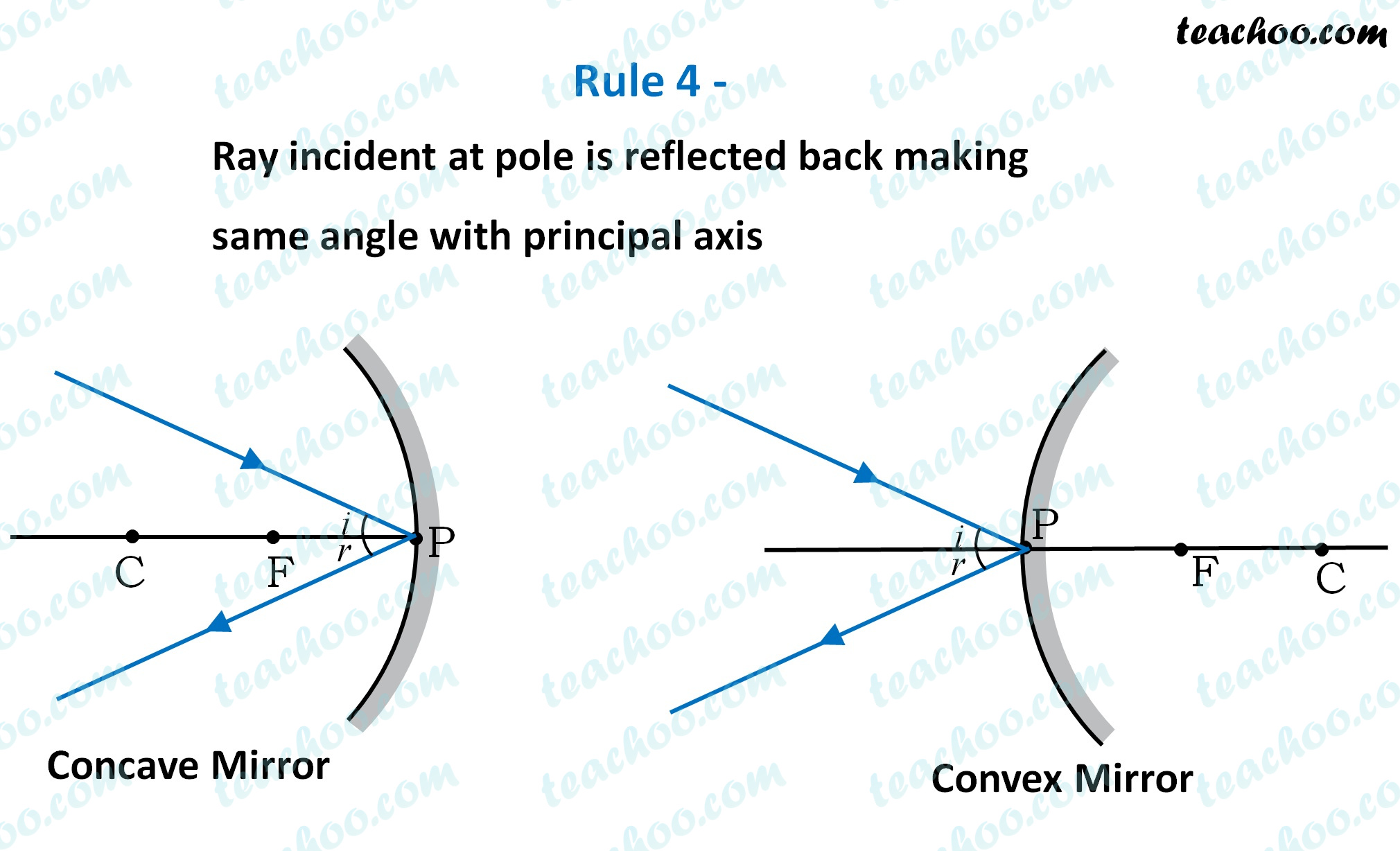
For both concave and convex mirror ,
if the incident ray to the Pole makes an angle of incidence i,
then it will go back making an angle of reflection r
with Principal axis as the normal
and Angle of Incidence = Angel of Reflection